|
CBSE
ANNUAL PAPER - 1999
PHYSICS
(SET-I)
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question are
indicated against it.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to 8 are
very short - answer questions, carrying 1 mark each. These are
to be answered in one or two sentences.
(iv) Questions numbers 9 to 18 are
short - answer questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to
these questions should be around 30 words each.
(v) Questions numbers 19 to 27 are
also short - answer questions, each carrying 3 marks each.
Answer to these questions should be around 50 words each.
(vi) Questions numbers 28 to 30 are
long - answer questions, each carrying 5 marks. Answer to these
questions should around 100 words each.
(vii) Use Log Tables, if necessary.
|
| Q.1. |
Draw an equipotential
surface in a uniform electric field. |
| Ans. |

|
| Q.2. |
If a wire is stretched to
double its original length without loss of mass, how will the
resistivity of the wire be influenced? |
| Ans. |
Resistivity will not change.
|
| Q.3. |
Why do magnetic lines of
force prefer to pass through iron than through air?
|
| Ans. |
This is because magnetic permeability of iron is
much higher than that of air. |
| Q.4. |
What is the power factor of
an LCR series circuit at resonance? |
| Ans. |
At resonance, power factor = 1. |
| Q.5. |
Why is the transmission of
signals using ground waves restricted to frequencies upto 1500 KHz?
|
| Ans. |
This is because the waves having frequency
higher than 1500 KHz get largely absorbed during their propagation
near the ground. |
| Q.6. |
The polarizing angle of a
medium is 60o. What is the refractive
index of the medium ? |
| Ans. |
Refractive index = tan ip = tan 60o = (3)1/2 |
| Q.7. |
How does the collector
current change in a junction transistor, if the base region has
larger width? |
| Ans. |
Collector current decreases. |
| Q.8. |
Two stars A and B have
magnitudes -2 and + 4 respectively. Which star appears brighter ?
|
| Ans. |
Star A appears brighter than B. |
| Q.9. |
An electric flux of -6 X 103 Nm2/C passes normally through a
spherical Gaussian surface of radius 10cm, due to a point charge
placed at the centre.
What is the charge enclosed by
the Gaussian surface?
(ii) If the radius of the
Gaussian surface is doubled, how much flux would pass through
the surface ?
|
| Ans. |
(i) By Gauss's theorem,
Æ
B + q/e
0 q =
e0 Æ B =
8.85 x 10-12 x (-6 x 103) = -53.1 x 10-9 C.
= -53.1 nC.
(ii) Since the charge enclosed is same in both coses,
therefore, Æ B
= -6 x 103 Nm2 C-1. |
| Q.10. |
Three identical resistors,
each of resistance R, when connected in series with a d.c. source,
dissipate power X. If the resistors are connected in parallel to the
same d.c. source, how much power will be dissipated ?
|
| Ans. |
The equivalent resistance when in series is 3R.
i = V/3R where i is the total current through the circuit. Power
dissipated = Vi = V X V/3r = V2/3r =
X (Given) The equivalent resistance when in parallel is R/3.
Power dissipated = Vi = 3V2/R =
3 X 3 (V2/3R) = 9X [V2/3R= X] |
| Q.11. |
Define mutual induction.
State two factors on which the mutual inductance between a given
pair of coils depends. |
| Ans. |
Whenever the current is one coil (Primary coil)
changes, the magnetic flux linked with the second coil (Secondary
coil) changes and an induced E.M.F. is set up in the Secondary coil.
This phenomenon is called mutual induction. It depends on two
factors : (i) The number of turns in primary land secondary coil.
(ii) The material of iron core placed inside the coil. If the
core is of soft iron, then value of M increases. |
| Q.12. |
Light from a galaxy, having
wavelength of 6000 A, is found to be shifted towards red by 50 A.
Calculate the velocity of recession of the galaxy.
|
| Ans.
|
Velocity of recession of the galaxy will be v =
(Dl/l)X c = 50/6000 X 3 X 108 = 2.5 X
106 ms
-1. |
| Q.13. |
A converging lens has a
focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of materials of refractive
index 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3,
what will be its new focal length ? |
| Ans.
|
1/fa = (mg /m a -1) ( 1/R1 - 1/R2)
or 1/20 = (1.6/1 -
1) (1/R1 - 1/R2) ......(1)
I/fw = (mg /m w -1)
( 1/R1 - 1/R2) ...
..(2)
Dividing (1) by
(2), we get
fw / 20 = 0.6 x 1.3 x 20 / 0.3 = 52 cm. |
| Q.14. |
Draw a labelled ray diagram
to show the image formation in an astronomical telescope for normal
adjustment position. Write down the expression for its magnifying
power. |
| Ans. |
Magnifying power = Angle subtended by the final
image at the eye/Angle subtended by the object at the objective =
f0/fe
Tube length fo + fe = 36
magnifying power = fo/fe = 8
Solving we get fe = 4 cm.
and fo = 32 cm. |
| Q.15. |
The half-life of a
radioactive sample is 30 seconds. Calculate (i) the decay constant,
and (ii) time taken for the sample to decay to 3/4 th of its initial
value. |
| Ans. |
(i) Disintegration constant l = 0.693/T1/2 = 0.693/30 = 0.0231 s-1. (ii) By definition of half-life, 1/2 of the initial mass
remains undisintegrated in 30 seconds. 1/4 of initial mass remains
undisintegrated in next 30 seconds. so, 3/4 th of the initial mass
disintegrates in 60 seconds. |
| Q.16. |
Draw a logic circuit diagram
showing how a NAND gate can be converted into a NOT gate.
|
| Ans. |
When both the inputs of a NAND gate
are connected together, it gets converted into a NOT gate.
Both the inputs A and B will become low or high simultaneously.
For A = B, the truth table of NAND gate reduces
into that of NOT gate. Figure shows the logic circuit
for the realisation of a NOT gate from a NAND gate.
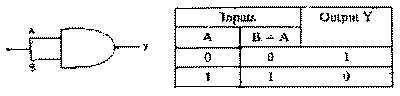
|
| Q.17. |
What is an ideal diode? Draw
the output waveform across R, for the input waveform given below :
|
| Ans. |
An ideal diode is one which offers
zero resistance during forward biasing and infinite resistance
during reverse biasing. The output wave form across R will be
as shown in the figure. |
| Q.18. |
Briefly describe, with the
help of a diagram, the method to determine the distance of an
inferior planet from the earth. |
| Ans. |
The angle formed at the earth
between the earth-planet direction and the earth - sun direction is
called the planet's alongation. This angle is denoted by symbol
Î as shown. When alongation attains its
maximum value Î, the
planet appears farthest - from the sun. In this position the
angle subtended by the sun and the earth at the planet is 900. rps / res = sin e
Distance of the planet from the sun is
rps = sin e. res =
sin e . AU
whese res = IAU = average earth
- sun distance.
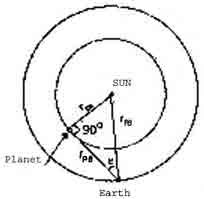
|
| Q.19. |
Explain, with the help of a
circuit diagram, the use of potentiometer for determination of
internal resistance of a primary cell. Derive the necessary
mathematical expression. |
| Ans. |
The resistance offered by
electrolyte inside the cell circuit is called internal resistance of
cell. Let there be a cell of emf E, internal
resistance r, used to draw current in a circuit of resistance r.
then
I = E/R+r
IR + Ir = E
IR + IR = E
Ir = E-V
Or r = E-V/I
Or r = (E-V)R/V .....(i)
EMF is maximum P.D. obtainable by a cell when it
is in open circuit.
The internal resistance of a primary cell can be
determined by potentiometer. The circuit is shown below :
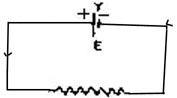
First insert infinite resistance from Resistance
box and find null diflection length (l1). Since the cell is in
open circuit.
E = Kl1
.............. (ii)
Now insert a know resistance R from Resistance
box and again find null deflection lelngth (l2). Since now the
cell is in closed circuit so.
V = Kl2 ............(iii)
By (i) r = (l1-l2) /R/l2
Thus internal resistance of cell is determined.
|
| Q.20.
|
Calculate the resistance
between A and B of the given network. |
| Ans. |
Given circuit is equivalent to
Wheat stone bridge shown in the figure.
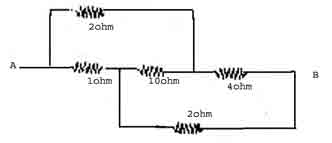
As 2W / 4W = 1W/2W
The bridge is balanced. The 10 W resistance is not effective. We have (2W + 4W) and ( 1W+ 2W) resistances in parallel.
\ 1/R =
1/6 + 1/3 = 1/2
or R = 2 W
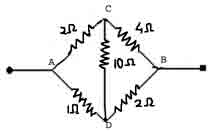 .
. |
| Q.21. |
State Faraday's law of
electrolysis. Write down the relation connecting chemical equivalent
and electro-chemical equivalent. |
| Ans. |
Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis : First law : The mass of a
substance deposited at the cathode during electrolysis is directly
proportional to the total charge passing through the electrolyte. m
= zq = z lt Second law : If same quantity of electricity is passed
through different electrolysis, masses of the different substances
deposited at the respective electrodes are proportional to their
chemical equivalents. m1/m2 = E1/E2 If E1 and E2 are
chemical equivalents and z1 and z2 are the electrochemical
equivalents of two substances, then E1/E2 = z1/z2
|
| Q.22. |
An electron is moving at
106 m/s in a direction parallel to a
current of 5 A, flowing through an infinitively long straight wire,
separated by a perpendicular distance of 10 cm in air. Calculate the
magnitude of the force experienced by the electron.
|
| Ans. |
B =m0I / 2p = 4
p x 10-7
x 5/ 2p x 10 x 10-2 =
10-5 T F = qvB SIN 900 = 1.6 x 10-19 x 106 x 10-5 x
1
= 1.6 x 10-18 N. |
| Q.23. |
A bar magnet, held
horizontally, is set into angular oscillations in Earth's magnetic
field. It has time periods T 1 and T2 at two places, where the
angles of dip are q1 and q2 respectively. Deduce an expression for
the ratio of the resultant magnetic fields at the two places.
|
| Ans. |
At first place, T1 = 2p (1/mH1)1/2 = 2p ( 1/mB1 cosq1) 1/2
At second place,
T2 =
2p (I/mH2)1/2 = 2p (1/mB2
cosq2)1/2
T1 /T2 = (B2
cosq2/ B1
cos cos q1)
or
B1 / B2 = T 2/2
cosq1 / T 2/1
cosq1
|
| Q.24. |
Verify Snell's law of
refraction using Huygen's wave theory. |
| Ans. |
Let the surface AB represent a
surface of separation of two media in which velocities of light are
c1 and c2 respectively. Let the wave front PQ be incident at an angle i
to the surface AB. By the time Q reaches surface AB at S, the
disturbance at P reaches R such that RS is the refracted wavefront.
The time taken by a ray to travel from T to U is
t = TO / C1 +
OU/C2
= PO sin i /C1 +
OS.sin r / C2
= PO SIN R /C1 +
(PS - PO) sin r / C2
t = PO (sin i /C1
- sin r /C2) + PS. sin r / C2
As the new wavefront is the forward envelop of
all secondary wavelets, this implies that the time taken is
independent of the position of O on the surface. Therefore,
for t to be independent of O,
sin i / c1 - sin
r/c2 = c
or sin i / sin r = c1/c2 = constant
(m)
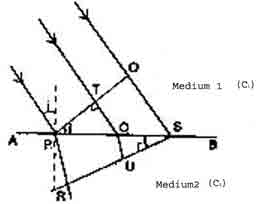
|
| Q.25. |
Find the position of an
object which when placed in front of a concave mirror of focal
length 20cm, produced a virtual image, which is twice the size of
the object. |
| Ans. |
For virtual image v/u =
-2 or v = -2u As 1/u
+ 1/v = 1/f
so,
1/u - 1/2u = 1/f or 1/2u = 1/f
or u =
f/2 = -20/2 = -10 cm. |
| Q.26. |
If the frequency of the
incident radiation on the cathode of a photo cell is doubled, how
will the following change : (i) Kinetic energy of the
electrons.
(ii) Photoelectric current,
(iii) Stopping potential.
|
| Ans. |
(i) If the frequency of the incident radiation
is doubled, the K.E. of the photoelectron becomes more than double.
As the work function of a metal is fixed, so incident photon of
higher energy will impart moe K.E. to the photoelectron. (ii) Increase in the frequency does not change the
photoelectric current. This is because incident photon of higher
energy will not be able to eject more than one electron from the
metal surface.
(iii) With the increase in frequency, K.E. of photoelectron
increases, so stopping potential also increases. |
| Q.27. |
Explain, with the help of a
circuit diagram, why the output voltage is out of phase with the
input voltage in a common emitter, transistor amplifier.
|
| Ans. |
Figure shows the circuit diagram
for n-p-n transistor used as common emitter amplifier. The
emitter-base circuit is forward biased and collector-emitter circuit
is reverse biased. The input Vi
is superimposed on the forward bias. the load RL is connected between collector and
emitter.
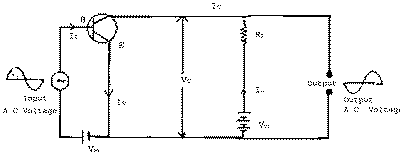
When a.c. signal is applied, the potential drop
between collector and emitter is given by :
V0 = VCE = VCC -
ICRL
The positive half cycle of input a.c. voltage
increases forward bias which increases the emitter current and hence
the collector current. The increase in the collector
current increases the potential drop across RL which makes the output voltage less positive, thus
giving negative a.c. output.
The negative half cycle of input a.c. voltage
decreases the forward bias which decreases the emitter current and
hence the collector current. The decrease in collector
current decreases the potential drop across RL which makes the output voltage more positive, thus
giving positive a.c. output. Hence the output voltage is
1800 out of phase with the input
voltage. |
| Q.28. |
With the help of a labelled
diagram, describe Millikan's oil-drop experiment for determining the
charge of an electron. |
| Ans. |
The experimental arrangement used
in Milikan's oil drop experiment is shown below :
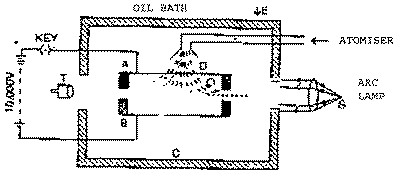
Here A and B are two optically plane metallic
discs of about 20 cm in diameter kept 1.5 cm apart. The upper plate
A has a pin hole O in its centre. The plates are arranged
inside a circular metal chamber, provided with two equally spaced
windows around it, and is surrounded by an oil bath to keep its
temperature constant. A high potential difference of the order
of 10,000 volts is established between plates A and B.
|
| Q.29. |
Draw the curves
showing the variations of inductive reactance and capacitive
reactance, with applied frequency of an a.c. source. A capacitor,
resistor of 5 W, and an
inductor of 50 mH are in series with an a.c. source marked 100V, 50
Hz. It is found that voltage is in phase with the current. Calculate
the capacitance of the capacitor and the impedance of the
circuit. OR
State Huygen's postulates of wave
theory. Sketch the wavefront emerging from a (i) point
source of light and (ii) linear source of like a slit.
|
| Ans. |
Huygen's postulates of wave theory
are as follows : (i) Every point of the medium situated on the
wave front acts a new wave-source from which waves, called secondary
wavelets, originate.
(ii) The secondary waveletes travel in the
medium in all directions with the speed of light.
(iii) The envelope of the secondary wavelets in
the forward direction at any instant gives the new wavefront at that
instant. |
| Q.30. |
Explain the effect of
introducing a dielectric slab between the plates of a parallel plate
capacitor on its capacitance. Derive an expression for its
capacitance with dielectric as the medium between the
plates.
OR
Give the principle and
explain the working of a van de Graaff generator with the help of a
labelled diagram. |
| Ans. |
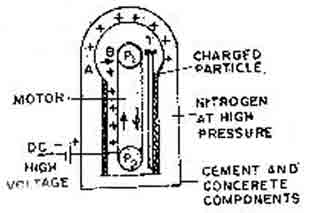
Van de Graff Generator - It is a
device to produce high voltage so that charged particles may be
energised. It consists of a large bellow metal sphere A
placed on insulting supports. An insulating belt moves
over pulleys P1,P2. The positive charge is leaked on the belt
from high voltage source. When the pulleys are driven with the help
of motor the positive charge moves along with belt. As the
charge enters the hollow sphere, +ve charge is induced on
outer surface while negative on the inner surface. The inner
surface charge is neutralised by +ve charge with the help of brushes
B. As more and more charge is induced on the sphere its
positive potential goes on increasing. To protect the
leakage of charge to atmosphere the whole apparatus is enclosed in a
cement and concrete compartment with high pressure nitrogen gas
filled in. The positive charge or ions to be energised are
placed in a long tube T.
|