|
CBSE ANNUAL PAPER - 1999
CHEMISTRY
(SET-I)
Time
allowed : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are
compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question
are indicated against it.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to
10 are very short-answer questions each of 1
mark. Answer them in about one sentence each.
(iv) Question numbers 11 to
26 are short - answer question of 2 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 30 words each.
(v) Question numbers 27 to
32 are short - answer questions of 3 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 40 words each.
(vi) Question numbers 33 and
34 are long-answer questions of 5 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 70 words each.
(vii) Use Log Tables, if
necessary. |
| Q.1. |
Give the maximum number of electrons which
can be accommodated in a set of (i) p-orbitals
and (ii) d-orbitals.
|
| Ans. |
There can be 6 electrons in
a set of p-orbitals and 10 electrons in a set of
d-orbitals.
|
| Q.2. |
What is an 'orbital' in an atom ? What does
the angular momentum quantum number tell about
on orbital ?
|
| Ans. |
An atomic orbital refers to
three- dimensional regions around the nucleuis
in which there is high probability of electron
of given energy being found is maximum.
Angular quantum number (l)
describes the shape of the electron cloud or the
shape of the orbital.
|
| Q.3. |
What is meant by 'Point Defects' in
crystals ?
|
| Ans. |
When any of the particles of
a crystal lattice is either missing or is
dislocated from its original position called
interstitial site we get point defect schottky
or Frioendkel defect.
|
| Q.4. |
Name any two metals, which can be used for
cathodic protection of iron.
|
| Ans.
|
Magnesium and zinc metals
can be used for cathodic protection of iron from
rusting. |
| Q.5. |
Define an 'ideal
solution'. |
| Ans. |
Two liquids A and B from an
ideal solution if A-A and B-B interaction forces
are the same and there is no net change in
molecular interaction forces A-B due to
identical structure and polarity of molecules of
A and B. An ideal solution will obey Raoults
law. |
| Q.6. |
Write two uses of selenium metal.
|
| Ans. |
Selenium finds use in
xerography, in photoelectric cells and as a
rectifier in semi conductor devices.
|
| Q.7. |
In the formula Fe (h5 - C5H5)2,
what does the prefix 'h5 indicate
? |
| Ans.
|
In the formula Fe
(h5 - C5H5)2,
the prefix
h5 means that all the five carbon
atoms of cyclopentadiene are bound to the metal
atom. |
| Q.8. |
Why are fusion reactions in
nuclear chemistry referred to as thermonuclear
reactions ?
|
| Ans. |
Fusion reactions require
high temperature (> 106K) to overcome
electrostatic repulsions between nuclei when
they come together to fuse. Hence nuclear fusion
reactions are called thermonuclelar reactions.
|
| Q.9. |
What are lipids and how are they classified
?
|
| Ans. |
Lipids are esters of long
chain fatty acids and alcohols. They are found
in all living organisms. Lipids are classified
as (a) simple lipids or triglyeerides and waxes
which on hydrolysis produce fatty acids,
alcohols, glycerol etc.) and (b) complex lipids
(Phospholipids) which produce glycerol, fatty
acids, phosphoric acid and choline etc - on
hydrolysis example lecithin.
|
| Q.10. |
What are the two most important oxidation
states of Group 6 elements of the periodic table
?
|
| Ans. |
Group 6 elements show
important oxidation states of 3 and 6 example
Cr3+ IN Cr2 (So4)3
and Cr6+ CrO3.
|
| Q.11. |
Explain the following observations :
(i) CO2 and SiO2
are not
isostructural.
(ii) O2 is
paramagnetic but O2/2- is not.
|
| Ans.
|
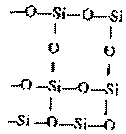
CO2 is a linear molecule with zero
dipole moment. It is represented as O = C = O.
This is due to the small size of carbon atom
which can form C = O by p p-pp lateral overlap.
In silicon dioxide (SiO2) silicon and oxygen
atoms are held together by strongcovalent bond
forces forming a three dimensional net - work
structure. Each silicon atom is tetrahedrally
bonded to four oxygen atoms. Larger
size silicon atoms cannot form bonds unlike
carbon atoms. It cannot form O = Si = O
structure.
|
| Q.12. |
Calculate the value of Avogadro number from
the following data :
Density of KF =
2.48 g cm-3
Distance between
K+ AND F- in KF = 269 pm
(Atomic masses :
K = 39 and F = 19 amu)
|
| Ans. |
Distance between K+ and F- =
269 pm Edge
length (a) = 2 x 269 = 538 pm.
=
538 x 10-10 cm
Mass
of K+ F- unit = 39+19=58=(M)
Density of KF = 2.48 g cm-3
(z)
no of K+ F- units in KF crystals = 4k+ F- = 4
N0 = ?
r Z x M /
a3 x N0 N0 = Z x M / a3 x r
= 4 x 58 / (538 x 10-10)3 x 2.48
= 6.02 x 1023 atoms mol-1
|
| Q.13. |
(i) What is osmotic pressure and how is it
related to the molecular mass of a non-volatile
substance ?
(ii) What advantage the
osmotic pressure method has over the elevation
of boiling point method for determining
molecular masses ?
|
| Ans. |
Osmotic pressure is the
measure of the external pressure which has to be
applied on the surface of the solution to
prevent osmosis of the solvent molecules through
the semi permeable membrane which separates the
solvent and the solution.
formula to be inserted.
(b) ADVANTAGE OF OSMOTIC
PRESSURE METHOD OVER THE ELEVATION OF BOILING
POINT METHOD FOR DETERMINING MOLECULAR MASSES.
(i) Elevation of boiling
point for measuring the molecular masses of
macromolecules like protein can not be used
because they are not stable at high temperature.
On the other hand the Osmotic pressure
measurements can be taken at room temperatures.
(ii) For very dilute
solution osmotic pressures are of the order of
atmosphere. This makes accurate measurements of
osmotic pressure quite convenient for dilute
solution.
TB values
are of the order of 10-5 which are too small to be measure
accurately by any instrument.
|
| Q.14. |
Calculate the molarity and molarity of a
13% solution (by weight) of sulphuric acid ? Its
density is 1.020 g cm-3.
[ Atomic masses
: H=!, O=16, S=32 amu)
|
| Ans.
|
13 % of solution of
sulphuric acid contains 13 g of H2SO4 in 100 g of the solution. Weight of
water = 100 - 13 = 87 g.
mole
of H2SO4 = 13/98
mole
Volume of H2SO4
solution + Weight of soluton / Density =
100/1.02 ml
=
100 / 1.02 x 1/1000 = 1/1.02 litre
Molarity of H2SO4
solution = mole of H2SO4 /
Volume of solution
=
13/98 / 1/1.02 = 10.2 x 13/98 = 1.353 M
Molality of H2SO4
solution = mole of H2SO4 /
wt of water in kg. = 13/98 / 87/1000 = 13/98 x
1000/87
=
1.525 mol kg-1
(mole Kg-1)
|
| Q.15. |
For the reaction at 500 K
NO2 (g) + CO
(g) -- CO2 (g) +
NO (g)
the proposed mechanism is as below :
(i) NO2 + NO2 -- NO + NO3
(slow)
(ii)
NO3 + CO --
CO2 + NO2 (fast)
What is the rate law for the reaction ?
|
| Ans. |
For the reaction
NO2 (g) + CO
(g) -- CO2 (g) +
NO(g)
Rate
mechanism is (i) NO2 + NO2 --NO + NO3 (slow)
(g) (g) (g) (g)
(ii)
NO3 + CO -- CO +
NO2 (g)
(g) (gas)
This shows that (i) is the
slow step in he reaction. This is the rate
determining step. Rate mechanism of the reaction
shows that rate law is Rate = K [ NO2] [ NO2] = K [ NO2]2
|
| Q.16. |
Derive the following
relationship : DG = -TDStotal |
| Ans. |
For an open
system DS(total) + DS(system) +DS9(surroundings) ....(1)
At
constant temperature and pressure heat is given
out of the surroundings
DS surrounding = -Qp
/T = - DH / T ( Since Qp =
DH at constant pressure)
= heat lost by
surrounding)
From (1)
DStotal + DSsystem = DH / T
Multiplying both sides by T
TDStotal = TDS(system) -
DH
......(3)
or - TDS total = DH -
TDS .......(4)
Also free energy change
DG = DH -
TDS
Hence for a change conducted
at constant temperature and pressure
From (3) and (4)
DG = -TDStotal
|
| Q.17. |
Write the IUPAC names of the following
compounds :
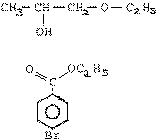
|
| Ans. |
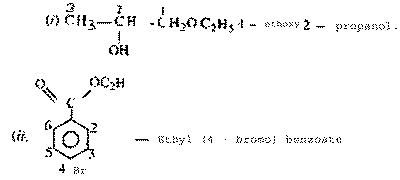
|
| Q.18. |
Find the two - third life, t2/3 of a first order
reaction in which k = 5.4 x 10-14S-1 2.
|
| Ans.
|
K = 5.4 x
10-14 s-1
For
t2/3 = let
initial concentration = 1 mol L-1
Final concentration = 1 - 2/3 = 1/3 mol
1-1
By
the relation t 2/3
= 2.303 / K log a/a-x
=
2.303/ 5.4 x 10-14 x log 1/ 1/3
=
2.303 / 5.4 x 10-14 x log 3
=
2.303 x 0.4771 / 5.4 x 10-14
=
2303 x 4771 / 54 x 108
= 2
x 1013 seconds
|
| Q.19.
|
What are transition elements? Account for
the following
(i) Transition elements have high
enthalpies of atomisation
(ii) Most of the compounds formed by
transition elements are coloured.
(iii) Transition metals form complex
compounds.
|
| Ans. |
Transition metals are
elements of d-block which form at least one
stable ion which has partially filled
d-orbitals. Example Cu2+ (3d9 4S0)
therefore copper is a transition element.
(i) In transition metals
both as electrons and unpaired electrons in
(n-1) d orbitals take part in d-d metal bonding.
Since in these elements metal bonding is
stronger than other elements of S and P block
the transition elements have high enthalpies of
atomisation.
(ii) In transition metal
ions the unpaired electrons in (n-1)d orbitals
absorb radiations from the visible range in d-d
transition. They emit coloured radiations
complementary to the coloured radiations
absorbed by them in under-going transitions.
Examples Cu2+
ions are blue coloured. Ni2+ salts are green. Sc3+ (3d0 4S0) ions are colourless as there is
no unpaired electron in 3d orbitals.
(iii) In transition metal
ions there are empty or vacated d-orbitals of
appropriate energy which can accept Ione pair of
electrons from neutral or negatively charged
ligands resulting in the formation of complexes.
Examples : [ Ni (CN4]2-,
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ and [ Fe (CN)6]4-
|
| Q.20. |
Write the complete reactions involved in
(a) the isocyanide test, and in (b) the iodoform
test.
|
| Ans.
|
Isocyanide test for
distinction between primary and secondary amines
:
RNH2 + 3KOH + CHCl3 + +
D RN = C + 3 Kel + 3 H2O Only 10 ammines having - NH2 group give foul
smelling isocyanides.
(ii) IODOFORM TEST FOR
ALCHOL having CH3
--- CH --- function
|
OH
and for aldehydes and
ketones having CH3 ---C--(R or H)
||
O
CH3 -- CH --- R + 3I2 + 4NaOH +D
CHI3 +
RCOONa + 3Nal +
4H2O)
| (Yellow iodoform)
OH
CH3 ----C---R+ 2I2 + 4NaOH +D
CHI + RCOONa
+ 3 Nal + 3 H2O
||
O
|
| Q.21. |
What
are nucleotides ? Name two classes of nitrogen
containing bases found in
nucleotides. |
| Ans. |
(i) Nucleotides are basic
components of nucleic acid. They contain II. a
phosphate ---sugar ---base ---unit. sugar may be
ribose or deoxribose. The bases - adenine,
guanine, cytosine, uracil or thymine are
attached to sugar molecule at No. 1 carbon atom.
(ii) Two classes of nitrogen
containing bases found in nucleotides. are (a)
Purines (Adenine and guanine and (b) Pyrimidines
( uracil, thymine and cytosine).
|
| Q.22. |
Write the equations for the synthesis of
(i) Neoprene and (ii) Glyptal. Which one of the
two is a condensation polymer
? |
| Ans. |
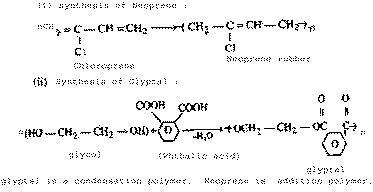 |
| Q.23. |
Giving a suitable example describe the
importance of the formation of complex compounds
in (a)
The estimation of hardness of water, and
(b)
the extraction of a particular metal from its
natural source.
|
| Ans. |
(a) Importance of
Co-ordination (complex) compounds in (i)
estimation of hardness of water. Hard water
contains Ca2+ and
Mg2+ ions which
form high stability complexes with hexadentate
ligand EDTA. The selective estimation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in hard water
can be done because there is a large difference
in the stability constants of Ca2+ and Mg2+ with EDTA.
(b)
Extraction of metals like gold and silver from
their ores by formation of their complex
compounds (soluble in water) whereas their ores
are insoluble in water.
Ag2S(ore) |
4NaCN -------> 2NalAg[CN2] Na2S
(insoluble) (Soluble
complex)
From
these complexes the metals can be precipitated
by adding Zinc dust (powder).
|
| Q.24.
|
What
do you understand by 'broad spectrum
antibiotics'? Is penicillin a broad spectrum
antibiotic ? Name a place in India where
penicillin is manufactured.
|
| Ans. |
(i) Chloramphenicol,
tetracycline like antibiotics which can be used
for curing a large number of infections are
called broad spectrum antibiotics.
(ii) Penicillin is a narrow
spectrum antibiotic.
(iii) It is manufactured in
India at Hindustan Antibiotics in Pimpri and
I.D.P.L. at Rishikesh
(U.P.). |
| Q.25. |
(i)
What is 'photosynthesis' and where does it occur
in plants? (ii)
Name the two products of photosythesis which are
needed by most chemotrophs for their survival.
|
| Ans. |
(i) The process of
conversion of Solar energy into chemical energy
in which plants produce organic molecules like
carbohydrates and amino acids 6H2O + 6CO3 ---> C6H12O6+6O2
is called photosynthesis. It takes place in
sunlight. The phenomenon of
photosynthesize takes place in chloroplasts of
plant cells which contain green pigment called
chlorophyl.
(ii) Two important products
of photosynthesis are carbohydrates - glucose,
starch. etc and amino acids which the
chemotrophs need for their survival.
|
| Q.26. |
Write nuclear reactions for the following
transformations :
(a) 238/92 U undergoes a-decay.
(b) 234/91 Pa undergoes
b-decay. |
| Ans. |
(a) 238 / 92 U
-------------> 4/2 He + 234/90 Th
(b)
234/91 Pa --------------> 0/-1e + 234/92 U
|
| Q.27. |
(i) Using the data given
below calculate the value of equilibrium
constant for the reaction at 298 K.
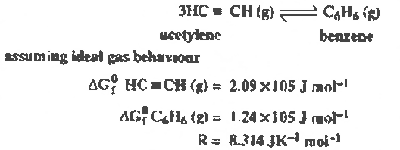
|
| Ans. |
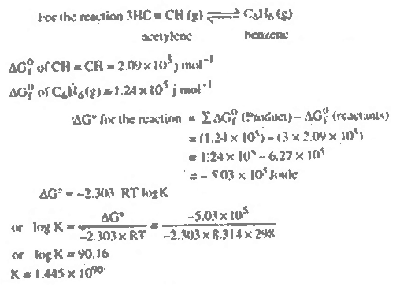
Large value of K shows that
this process can be recommended as a practical
method for preparing benzene from acetylene.
|
| Q.28.
|
Write the structure of the main product of
each of the following reactions :
(i)
Chlorination of benzene in the presence of ultra
violet light.
(ii)
Action of excess of bromine on phenol.
(iii) Action of alkaline potassium
permanganate on ethane.
|
| Ans.
|
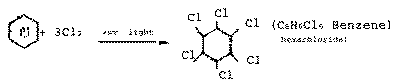
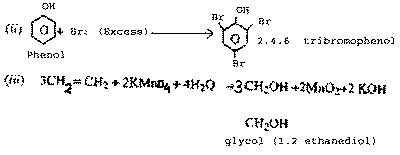
|
| Q.29. |
Account for the following :
(i)
Chloroacetic acid has lower pKa value than
acetic acid.
(ii)
Electrophic substitution in benzoic acid takes
place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids have higher boiling
points than alcohols of comparable molecular
masses.
|
| Ans.
|
(i) Due to greater stability
of chloroacetate ion than acetate ion owing to
CH2 --COOH
is > KA
electron with drawl effect of -----------cl
group. KA of Cl
of acetic acid. Hence PKA of chloroacetic acid
is less than PKA
of acetic acid.
(ii) -COOH group in benzoic
acid is an election with drawing group. By
inductive effect -COOH group. Hence
electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes
place at meta position.
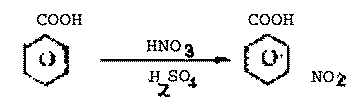
(iii) Carboxylic acid have
higher boiling points than alcohols of
comparable molecular masses because they form
dimers on intermolecular hydrogen bonding CH3COOH has higher
boiling point than C3H5OH.
In dimers two carboxylic acid molecules are held
through Hydrogen bonds.
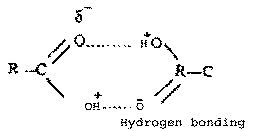
|
| Q.30. |
Write chemical equations for the conversion
of : (1) chromate
ore to sodium chromate.
(2) Pyrolustile
to potassium manganate.
(3) Potassium
permanganate to manganese
dioxide. |
| Ans.
|
(i) 4Fe -
Cr2O3) + 16 naOH + 7o2 fuse 8Na2 Cro4
+ 2FE2O3 + 8H2O Chromite + D Sodium
chromate
(ii)
2MnO2 + 4 KOH
O2 -------> 2
K2 MnO4 + 2H2O
Pyrolusite ore (Potassium manganate)
(iii) 4 K MnO4 + 2H2O -->4 KOH + 4 Mno2 + 3O2
(
Pot permanganate)
|
| Q.31. |
Calculate the EMf of the
cell. at 298 K PT BR2 (I)
IBr-1 (0.01 M) ||
H+ (0.03 M)
IH2 (1 atm|Pt
Given E0
Br|br - = 41.08 V. |
| Ans |
The cell notation is wrong
because the lower value of EO of electrode will serve as anode.
hence.
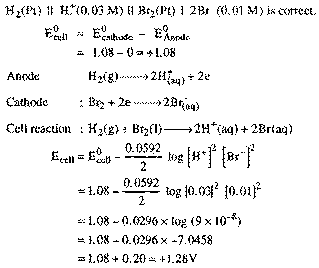
|
| Q.32. |
(i)
Explain the meaning of the statement,
"adsorption is a surface phenomenon."
(ii)
State two features of chemical adsorption which
are not found with physical adsorption.
|
| Ans. |
(i) In adsorption the
molecules of a liquid or a gas get concentrated
only on the surface of the solid. The surface of
the solid possesses particles with unbalanced
forces like weak vanderwall forces or chemical
bond forces. On breaking a piece into two parts
two new surfaces are formed which attract more
molecules of liquid or gases. Adsorption in
creases with increase in surface area. Hence
adsorption is a surface phenomenon.
(ii) (a) Chemical adsorption
occurs at comparatively high temperature. It
first increases due to requirement of activation
energy. (like all chemical reactions.) in
initial stages. Physical adsorption. takes place
at low temperature. It decreases on increasing
temperature.
(b) Chemical adsorption is
highly specific in nature but physical
adsorption is not as specific. Charcoal adsorbs
all gases physically but tungsten adsorbs oxygen
chemically.
|
| Q.33. |
(a)
Account for the following :
(i)
Like ammonia, amines are good nucleophiles.
(ii)
In contrast to arenas, aliphatic hydrocarbons do
not undergo nitration easily.
(iii) Alkylamines are stronger bases than
arylamines.
(b)
Illustrate the following reactions with an
example in each case :
(i)
Sandmeyer reaction
(ii)
Coupling reaction.
|
| Ans. |
(i) Like ammonia all amines
primary, secondary or tertiary contain lone pair
of electrons on nitrogen atoms. Hence amines are
good nucleophiles. Like ammonia they react with
alkylhalides undergoing nucleophilic
substitution reactions. C2H5Cl+CH3 --NH2 ------> C2H5NH
---CH3. They
displace weaker nueophile like Cl.
(ii) Aliphateic hydrocarbons
undergo nitration in drastic conditions. With
fuming nitric acid in the vapour phase at 423 to
673 K under pressure alkanes undergo under go
nitration.
CH4 +
HNO3 (funning)
673 K CH3 NO2 + H2O
This is
becaue nitration of alkanes occurs by free
radical mechanism. In arenes nitration is
through electrophilic substitution which is
easier.

(iii) In Alkyl animes the
alkl groups are strong electron pushing. By
their _1 effect the electron density on N-atom
of R-- NH2 is
increased but the benzene ring in C6H5 --- NH3 is electron attracting. C6H5 -- NH2 group decreases electron density on
N-atom. Hence alkyl amines are stronger bases
than aryl amines.
(b) (i) Sandmeyer's reaction
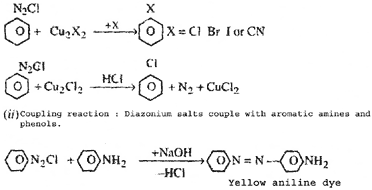
|
| Q.34. |
Present a comparative account of the
following :
(1) Structure
of beryllium chloride and aluminium chloride.
(2) Proton
affinities of NH3 and
PH3.
(3) Action of
water on CCl4 and
SiCl4.
(4) Physical
states of nitrogen and phosphorus.
(5) Shapes of
ClO2 and Cl2O
|
| Ans. |
(i) Beryllium Chloride has a
bridged structure with three centre bonding in
the solid state. It is polymeric chain
structure.
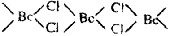
In
vapour phase Be Cl2 has liner geometry.
Alluminium chloride exists
as a simer Al2
Cl6 in which each
atom forms one co-ordinate bond by accepting
tone pair from the chlorine atom of another
AlCl3 molecule. This makes Aluminum to attain
complete octet.
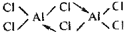
(ii) In ammonia : (NH3) the lone pair has
more affinity for proton H+ due to higher
electrogegativity and small size of N atom. Due
to the lower electronegativity and large size of
phosphorous atom (compared to nitrogen) the lone
pair on Phosphorous atom in : PH3 has lower affinity
for H+ (proton).
NH3 is more basic
than PH3.
(iii) Carbon tetrachloride does not react
with H2O due to
the absence of d-orbitals in the valence shell
of carbon (Is2
2s2 2p2). Silicon (Is2 2p6 3s2 3p2)
has d-orbitals in it valence shell hence Si
Cl4 is easily
hydrolysed.
Si Cl4 + 4
H2O ---> Si
(OH)4 + 4HCl.
Silicicx acid
(iv) Nitrogen is a gas it
exists as diatomic molecules. N2 with weak vander Wall forces
between them. Phosphorous has P4 molecules or P4 chains with stronger intermolecular
forces. Phosphorous is a solid at ordinary
temperature.
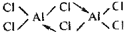
There is larger bond angle in O - Cl - O
than in ClO. Both are angular in shape.
|