|
CBSE ANNUAL PAPER - 1998
CHEMISTRY
(SET-I)
Time allowed : 3
hours
Maximum Marks :
70
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are
compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each
question are indicated against it.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to
10 are very short-answer questions each of 1
mark. Answer them in about one sentence each.
(iv) Question numbers 11 to
26 are short - answer question of 2 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 30 words each.
(v) Question numbers 27 to
32 are short - answer questions of 3 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 40 words each.
(vi) Question numbers 33
and 34 are long-answer questions of 5 marks
each. Answer them in not more than 70 words
each.
(vii) Use Log Tables, if
necessary. |
| Q.1. |
Why are all the P.F. bonds in PF5 molecule not of the
same length
? |
| Ans.
|
The molecule of PF5 has trigonal
bypyrimidal geometry with three equatorial
fluorine atoms close to the central phosphorous
atom than the two vertical fluorine atoms. Hence
all the five P-F bonds are of different
lengths. |
| Q.2. |
Name the type of structure processed by a
unit cell of CsCL. |
| Ans. |
Unit cell of cezium
chloride has body centered cubic crystal lattice
structure. |
| Q.3. |
Unit cell of cezium chloride has body
centered cubic crystal lattice structure.
23/11 Na.... ------> 23/12 Mg + )0/1 n
|
| Ans. |
23/11 Na + 1/1 H ---->
23/12 Mg. + 1/0 n |
| Q.4. |
Write the IUPAC name of the
following compound : CH3
--CO--CH--CH2-->CH2Cl
CH3 |
| Ans. |
CH3 --CO--CH--CH2-->CH2Cl
CH3
5 chloro 3
methyl 2 pentanone.
|
| Q.5. |
Which one of the following
elements exhibits + 1 oxidation slate as well
? Al, B,Ca, tl,
Be. |
| Ans. |
Thalium (Tl) exhibits + 1
onidation State State as well ( due to inert
pair effect). |
| Q.6. |
Why is copper sulphate pentahydrate
coloured ? |
| Ans. |
Copper
sulphate cuso4 -
5H2O has cu
(H2O)4 - SO4 - H2O structure. Due to
[cu (H2O)4]2+ Complexion it is blue in
colour. |
| Q.7. |
Write the IUPAC name of the
linkage isomer of [ Co(NH3)5
NO2] Cl2. |
| Ans. |
Linkage
isomers of [ Co(NH3)5
NO2] cl2 is
[Co(ONO) (NH3)5]
Cl2 |
| Q.8. |
What type of substance is phenylalanine
bydroxlase ? What is the importance for us
? |
| Ans. |
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
is an enzyme whose deficiency causes congenital
disease phenyketone
urea. |
| Q.9. |
What is the role of dimethyl and
monomethyl hydrazines in rockets
? |
| Ans. |
Dimethyl and monomethyl
hydrazines along with liquid N2O4 are used as liquid propellents in
rockets. |
| Q.10. |
Which category of dyes does alizarin
belong ? |
| Ans. |
Alizarine is an
anthraquinone dye, it is also a morodant
dye. |
| Q.11. |
In
the compound AX, the radius of A+ ion is 95 pm
and that of Ion is 181 pm. Predict the crystal
structure of AX and write the coordination
numbers of each of the
ions. |
| Ans. |
Radius A+ / X- = 95/181 =
0.5 Which lies between 0.414 - 0.732 A + X- has
octahedral crystallattice with co-ordination
numbers A + : X- as 6:6
each. |
| Q.12. |
Differentiate between molarity and
molarity of solution. When and why is molarity
preferred over molarity in handling solutions in
chemistry
? |
| Ans. |
Molarity of a solution
equals number of moles of solute in one litre of
the solution but molarity of a solution refers
to the number of moles of solute dissolved in
one kg. of the solvent. Molarity of a solution is
preferred for expressing the concentration in
procedures where temperature changes may occur
because molarity unlike molarity does not change
with temperature. Colligative properties like
depression of ferrzing point, D Tf and elevation of boiling point
DTb are proportional to
molarity DTb
a molarity and
DTf
a
molarity
|
| Q.13 |
Define the term 'entropy'. How does
TDS
determine the spontaneity of process ?
|
| Ans. |
Entrophy is the property of
a system which describes the disorder in it. The
more the disorder in the system greater its
entropy. For any spontaneous reaction DG should be negative By the
relation
DG =
DH -
TDS if
DH is + ve, this reaction will be spontaneous
only when DS is positive and TDS is greater than DH. Then
DG will be -ve. |
| Q.14. |
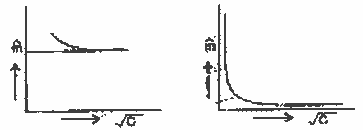
With the help of a graph expl [ question
to be inserted
] |
| Ans. |
For a strong electrolyte
the graphÙ m Vs
(C)1/2 the
concentration shows that at low concentration
Ù m , reach a limiting valve.
Extapulation of this line gives
Ù a/m of the electrolyte.
But for a weak electrolyte like CH3COOH there occurs a
steep rise in
Ù m with continuous decrease
in concentration. This is due to an increase in
the number of ions with continuous decrease in
concentration the graph shows that at no point
does it interest the line of infinite dilution
(c = 0)1/2.
Hence it is not possible to determine
µ Ù m of weak
electrolyte by graphic method.
|
| Q.15. |
Differentiate between
: (i) rate of
reaction and rate constant of a reaction.
(ii) order of
a reaction and its molecularity.
|
| Ans. |
|
(i) Rate of
reaction |
Rate constant
of reaction. |
(a) It refers to the rate
of change in the concentration of reactant or
the reactants. In Dx/Dt = k [A]m [B]x rate of reaction of reaction
dx/dt. |
(a) In the expression dx/dt
= x[A]m [B]n for the reaction A
+ 2B --- 3C K (constant ) is the rate constant
of the reaction. It is numerically equal to the
rate of reaction if concentration of reactant
(-s) is unity. |
(b) The units of rate of
reaction are mol L-1, S-1 for all orders of
reaction. |
(b) Units of K are
different for different orders k has units -
S-1 and for
second order L mol-1 S-1 for zero order reaction k has
same units as the rate of reaction ( mol L-1 S-1) |
(c) Rate of reaction
changes with change in the concentration
reactants. |
|
|
| ii. |
| Order of
reaction |
Molecularity |
1. Order of a reaction is
the sum of the exponents of concentration terms
of reactants as in experimentally deter-minded
rate equation for any reaction. Example if for
A+2 -- 3C. Rate =K[A]m X [B]n order of this reaction is (m+n)
|
1. Molecularity is equal
equal to the number of molecules as given in the
stoichiometric equation for the reaction. For A
+ 2B -- 3C molecularity = 1 + 2 = 3
|
2. Order of a reaction may
be a whole numbers or a fraction or
zero. |
2. Molecularity of a
reaction can only be a whole
number. |
3. It can be determined
experimentally with reference to the kinetic
data. It has no relation with the balanced
chemical equation for the
reaction. |
3. It is calculated by
simply adding the number of molecules of the
reactants in balanced chemical equation for the
reaction. |
|
| Q.16. |
Calculate the energy change in J/mol for
the nuclear reaction 0/1 n
-----> 1/1 p + 0/1 e
|
| Ans. |
For 0/1 n ----> 1/1 p +
0/1 e Decrease in mass = 1.00867 -
1.00728
=
0.00139 amu.
Energy change per atom = mc 2
=
0.00139 x 1.66 x 10-27 x (3 x 108 ms)2
Energy change per mole = 0.00139 x 1.66 x
10-27 x
(3x108)2 x 6.02 x 1023
=
1.24 x 10-27
Jmol-1
|
| Q.17. |
Account for the following
: (i) Haloarenes
are insoluble in water but are soluble in
benzene.
(ii) Phenols
are move acidic than alcohols.
|
| Ans. |
Haloarenes are insoluble in
water because they cannot break hydrogen bounds
between water molecules. They are however
soluble in benzene due to similar structure of
haloarene and benzene. (ii) Phenols are more acidic than alcohols
because the phenoxide ion C6H5O is more
stablised by resonance than phenol.
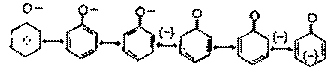
|
| Q.18. |
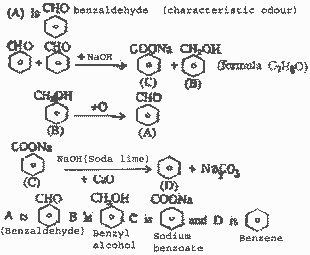
Anorganic compound (A) which has a
characteristic odour, on treatment with NaOH
forms two compounds (B) and (C). Compound (B) hs
the molecular formula. C7H8O
which on oxidation gives back compound (A).
Compound (c) is the sodium salt of an acid. (C)
when heated with sodalime yields an aromatic
hydrocarbon (D). Deduce the structures of (A),
(B), (C) and
(D). |
| ANS. |
 |
| Q.19. |
Suggest chemical tests to distinguish
between : |
| (i) |
propanol and
propanone |
| (ii) |
acetaldehyde and
benzaldehyde |
| Ans. |
(i) Propanol (CH3CH2CH2OH) Add iodine and dil NaOH solution and warm
no reaction.
Propanone
(CH3COCH3)
On boiling with I2 and NaOH
(aq) a yellow crystalline substance iodoform is
produced.
CH3C-CH3 I2+3NaoH
||
CH I3 + CH3
CooNa
O
(ii) Acetaldehyde ( CH3
CHO)
Add Fehling reagent Cuso4 + Naoh and warm. A reddish
precipitate is formed
2CU z+ 50H
+ CH3 CHO --
CH3COO + 3H2O + Cu2O
(red)
Benzaldehyde ( C6H5CHO)
on
warning with fehling solution C6H5CHO does not give any reddish
colour.
C6H5CHO + 50H + 2Cu 2+
-- No reaction
|
| Q.20. |
What is meant by 'Catenation'? How does
the catenation tendency for elements of group 14
vary ? |
| Ans. |
Catenation is the property
of interlinking of atoms of the same element to
from long, branched or cyclic
chains.
This phenomenon is shown by carbon,
sulphur and phosphorous.
- Tendency for contenation decreases in
going down group 14
C-C>Si-Si>Ge-Ge>Sn-Sn>Pb-Pb
This is due to decrease in the strength of
M-M bond C-C>Si-Si>Ge - Ge > Sn-Sn >
Pb - Pb
|
| Q.21. |
Using the Valence Bond approach, explain
the shape and magnetic behaviour of [Ni (NH3)6]2+. Given : At. No. of Ni =
28. |
| Ans. |
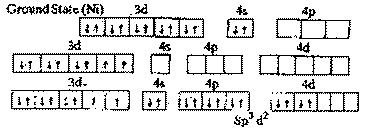
[
Ni(NH3)6]2+ has octahedral geometry because
the six pairs of electrons donated by 6 NH3 ligands are
accommodated in six sp3 d2
hyberdised orbitals of Ni2+.
There are two upaired
electrons in the complex (in 3d orbitals) It is
paramagnetic.
|
| Q.22. |
Calculate the standard free energy change
for the reaction occurring in the cell
: Zn(s) | Zn2+ (!M) || Cu2+ (1M) | Cu(s) [ Given E0 Zn2+ / Zn = -0.76V, E0 Cu2+ /Cu = +0.34 V; F + (^%))
Cmol-1]
|
| Ans. |
For the cell Zn : Zn2+ || Cu2+ : Cu(s)
(1M) (1M)
E0 cell =
C0 Cathode -
E0 Anode = +0.34
-(-0.76) = 1.10 Volt.
D G0 = nFE 0 ( Cell reactuib us Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) --- Zn2+ (aq) + CU0 (s)
= - 2x 96500 x 1.10
= - 212.3 K Joule.
Equilibrium constant K is related to free
energy change for the cell reaction by the
relation.
D
G0 =
-2.303 x RT log K = - nFE0
|
| Q.23. |
The decomposition of N2 in CCl4 solution
follows the first order rate law. The
concentrations of N2O5; measured at different
time intervals are given below : formula to be
inserted. |
| |
| Time in seconds (t)
|
0 |
80 |
160 |
410 |
600 |
1130 |
1720 |
|
| |
| |
[
N2O5]
mol/L |
5.5 |
5.0 |
4.8 |
4.0 |
3.4 |
2.4 |
1.6 | |
| |
Calculate its rate constant
at t = 410 s and t = 1130s. What do these
results show ? |
| Ans. |
For the decomposition of
N2O5 in ecl4 solution
: k
= 2.303 / t log a/a-x ( ist order
reaction)
K1
= 2.303 /410 log 5.5/4.0 = 7.708 x 10-3
k2
= 2.303 / 1130 log 5.5 / 2.4 = 7.401 x 10-3
|
| Q.24. |
Write
equations for the synthesis of the following
polymers : (a) Glypptal (b)
Teflon |
| Ans. |
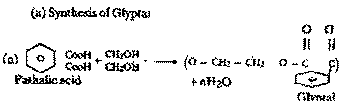 (b) Synthesis of Teflon
--------->
n(CF2 --
CF2) n
----------> (CF2--CF2) n
(Tetrafluro-ethylene) Teflon
|
| Q.25. |
Explain the term CONDON in relation to
mRNA. What are nucleotides
? |
| Ans. |
(i) Condon : mRNA has Adenine, guanine,
cytosin and uracil bases attached to ribose
sugar. Base triplet on m RNA chain which codes
for a specific ammino acid is called a
condon. (ii)
Nucleotides : A nucleotide consists of three
components.
(a) A five carbon atom sugar
Ribox/deoxyribox.
(b) A phosphate - PO4
(c) A nitrogenous base - adenine, guanine,
cytosine.
base
Uracil and thiamine :Sugar --Phosphate
Re[resemts miceptode/ |
| Q.26. |
What is genetic engineering ? In what
way are biotechnological products useful to
human beings? Illustrate with two
examples. |
| Ans. |
Genetic engineering is a
biotechnology involving enzymes which help in
inserting a section of a DNA molecule into an
organism ( bacterium) to synthesise newer
proteins with altered aminoacid
sequences. Biotechmoligal products are helpful to
human beings.
(i) Insulin is used for treatment of
diabetes.
(ii) interferon is anti viral agent.
|
| Q.27. |
In
what way Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
contradicts the concept of stationary orbit for
electrons as suggested by Bohr
? An
electron has a speed of 500 ms-1 with an uncertainty of 0.02 %.
What is the uncertainty in locating its position
?
[ Give mass of
electron = 9.1 x 10-31 kg, h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js]
|
| Ans. |
(a) The concept of
stationary orbits for electron suggested by Bohr
assigns a fixed position to an electron moving
round the nucleus whereas heisen - burg "it
is impossible to determine simultaneously and
accurately the position and momentum of the
moving electron. The position and momentum of
the moving electron. The position and momentum
of the moving electron in
uncertain. (b)D
V = 0.02 / 100 x 500
= 0.1ms-1
m = 9.1 x 10-31kg
m
DV x D x = h /4p x 1 /mDV
= 6.6 x 10-34 x 7 / 4 x 22 x 1 / 9.1 x
10-31x0.1
= 66 x 7 / 4x22x9113 x 10-34x10+31 x x 10
3/52 x 10-2 = 5.77 x 10-4
|
| Q.28. |
Assuming complete dissociation, calculate
the expected freezing point of a solution
prepared by dissolving 6.00g. of Glauber's salt,
Na2SO4. 10H2O in 0.100 kg
of H2O. [ Given
for water, Kr = 1.86 K kg mol-1 Atomic masses :
Na = 23, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1
amu] |
| Ans. |
Na2SO4 -----------> 2Na+ + SO4 (3 particles)
Molar mass of Na2 SO4 - 10H2O = 44 + 32 + 64 + 10 x 18 = 322.
Wa = Mass of H2O = 0.1 kg = 100
g
WB = Mass of the
solute = 6.0 g
Kf = 1.86 k kg.
mol-1 and i
(Vont Hof factor) = 3
By the relation
DTf = kf / MB x 1WB/WA x 1000 x i
= 1.86 / 322 x 6.0 / 100 x 1000 x 3 =
0.346k
Freezing point of
solution = 273 - 0.346 k = .654 k.
|
| Q.29. |
Calculate the standard free
energy change for the following reaction at
270 C.
f
H2 (g) + I2(g) -- 2HI (g)
; D H0 = + 51.9
kJ
[Given S0
H2 = 130.6JK-1
mol-1, S0 I2 = 116.7 JK-1
mol-1
S0 HI = 206.3
JK-1 mol-1
Predict whether the reaction is feasible
at 270 or not.
|
| Ans. |
D
S = S0
(products) - S0
(reactants) =
S0 (2HI) -
[S0(H2) + S0 (I2)]
=
2 x 206.3 - (130.6 + 116.7)
=
412.6 - 247.3 = 165.3Jk-1
DH0 = 51.9
kJ
= 51900 J
DG0 = DH0
- TDS0
= 51900 - 300
x 165.3
= 51900 - 49590 = 2310
Joule
Since DG0
is +ve the reaction is not
feasible at 300 k.
|
| Q.30. |
(a) Compare physical adsorption and
chemical adsorption in terms of rate and
prevailing
temperature. (b) Show graphically how the amount of a
gas adsorbed on a solid in physical adsorption
varies with (i) pressure and (ii) temperature ?
|
| Ans. |
| Physical
adsorption |
Chemical
Adsorption |
(1) Physical
adsorptions are instantaneous taking less than
0.01 seconds. |
(1) Chemical adsorption may
sometimes be quite slow depending upon the
nature of chemical reaction involved in
adsorption. |
(2) Physical adsorption
takes place at low temperature and decreases
with rise of
temperature. |
(2) Chemical adsorption
takes place at high temperature. It shows an
initial increase up to certain temperature. Then
decreases when the temperature is raised.
|
| b |
Figure to be
inserted
Physical adsorption
increases with increase in pressure but becomes
constant after certain limiting pressure.
|
|
| Q.31. |
How are the following conversions carried
out ? (Write reactions and conditions
only) (i)
1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
(ii) propanone
to iodoform
(iii) phenol
to salicylic acid
|
| Ans. |

|
| Q.32. |
Account for the following :
(i) NH3 has higher boiling
point than PH3
(ii) H3PO3 is a diprotic acid
(iii) OF2 should be called
oxygen difluoride and not fluorine oxide.
|
| Ans. |
(a) Due to high
electronegativity of nitrogen atom of NH3 its molecules are
associated through hydrogen bonds
H H H
| | |
H---N-----H---N-----H-----N--H
| |
H H
It has a higher boiling
point than PH3.
Phosphorous is less electrogengative than
nitrogen. No hydrogen bonds exist between PH3 molecules.
(b) Experiments show that
H3PO3 has reducing
properties. One of its three hydrogen atoms is
directly attached to P-atom as in the structure
H
|
HO-----O---OH
||
O
This H-atom is not ionised
while two other hydrogens are ionisable they
exist as - OH groups. This explains why H3PO3 is diprotic.
(c) in OF2 oxygen is electropositive with
respect to fluorine OF2 is called oxygen fluride and not
fluorine oxide.
|
| Q.33 |
What is vapour phase nitration ? Describe
the preparation of nitroalkanes and alkyl
nitrites from alkyl halides. Explain why the
boiling points of nitroalkanes are higher than
those of corresponding alkanes ?
How can the
following compounds be prepared :
(i0 Aniline
from nitrobenzene
(ii)
Ethylamine from nitroethane
|
| Ans. |
(i) Vapour phase nitration : Saturday
by hydrocarbons react with nitric acid in vapour
phase between 420 - 700 K when a mixture of
nitro derivatives is formed. 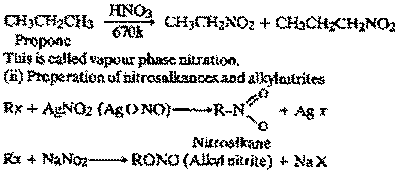
(iii) Boiling points of
nitro compounds are higher than the
corresponding hydrocarbons (alkanes ) because
alkanes are nonpolar whereas nitroalkanes are
polar compounds.
(iv) Conversions (i) aniline from
nitrobenzene

|
| Q.34. |
(a) Describe with the help of chemical
equations the preparation of potassium
dichromate from chromite ore.
(b) Give balanced chemical equations for
what happens when acidified potassium dichromate
solutions reacts with :
(i) ferrous
sulphate solution
(ii) hydrogen
sulphide gas
(c) Draw the
structure of Cr2O2/7- ion.
|
| Ans.
|
(a) For
preparing K2
Cr2 O7 from Fe Cr2 O4 ore : (i) Fusing chromite
ore with Na2 CO3 and lime as flux in excess of air
4FeCr2O4 + 8Na2CO3
+ 7O2 -- 8Na2 CrO4 + 2Fe O3 + 8CO2
(ii) Reacting Na2 CrO4 solution with conc
H2SO4 to get Na2, Cr2, O7
2Na2 CrO4 + H2 SO4 -- Na2 Cr2 O7
+ Na2SO4 + H2O
(iii) Addition of
KCI solution
Na2 Cr2 O7+ 2KCI -- K2Cr2
O7 + 2NaCl
( Less soluble)
(More soluble)
On cooling the hot
concentrated solution obtained in step (iii) the
less soluble K2Cr2
O7 separates as
orange crystals.
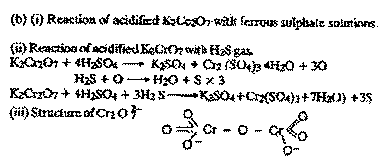
|