|
CBSE ANNUAL PAPER - 2000
CHEMISTRY
(SET-I)
Time
allowed : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are
compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question
are indicated against it.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to
10 are very short-answer questions each of 1
mark. Answer them in about one sentence each.
(iv) Question numbers 11 to
26 are short - answer question of 2 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 30 words each.
(v) Question numbers 27 to
32 are short - answer questions of 3 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 40 words each.
(vi) Question numbers 33 and
34 are long-answer questions of 5 marks each.
Answer them in not more than 70 words each.
(vii) Use Log Tables, if
necessary. |
| Q.1. |
What
is the physical significance of the lines in the
following depictions of atomic orbital :
|
| Ans. |

For an S- orbital the radial
electron probability is spherically symmetrical.
For a p-orbital the electron probability takes
the form of dumbell along along a coordinate
axis. |
| Q.2. |
An
ionic compound AB2 possesses CaF2 type crystal structure. Write the
co-ordination numbers of A2+ and B- ions in crystals of AB2.
|
| Ans. |
Co-ordination
number of A2+ = 8
and Co-ordination number of B- = 4. |
| Q.3. |
How
may the state of a thermodynamic system be
defined ? |
| Ans. |
State of a thermodyanamic
system is described by its measurable properties
like Pressure, Temperature, Volume and Moles.
they are cattled variables of
state. |
| Q.4. |
State Kohlrausch's law for electrical
conductance of an electrolyte at infinite
dilution.
|
| Ans. |
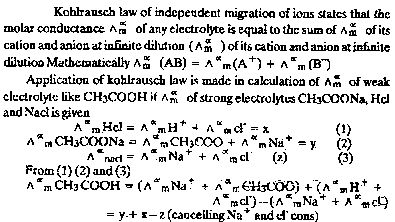
|
| Q.5. |
For the reaction 3H2 (g) + H2 (g) -- 2N3(g), how are the rate
of reaction expressions -d[H2]/dt and d[NH3] / dt interrelated ?
|
| Ans.
|
Rate of
reaction = -d[H2]/dtX3 = +d[NH3]/DtX2 |
| Q.6. |
Mention a use
of formalin in industry.
|
| Ans. |
Formalin (HCHO) is used in
the preparation of phenol formaldehyde resin
(bakelite). It is also used as a preservative
for biological specimens.
|
| Q.7. |
For
an amine RNH2
write the expression for Kb to indicate its base strength.
|
| Ans. |
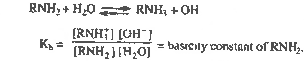
|
| Q.8. |
What
is responsible for the blue colour of a solution
of an alkali metal in liquid ammonia ?
|
| Ans. |
A solutions of alkali metal
in liquid ammonia has blue colour due to the
solvated electron present in the solution.
2M +
2NH3 --- 2M
NH2 + H2 ( M is alkali
metal)
e-1 + X
NH3 -- [ e -
(NH3)x]-1
|
| Q.9. |
Why do
colloidal solutions exhibit Tyndall effect ?
|
| Ans. |
Colloidal solutions are
heterogeneous in nature. They exhibit Tyndall
effect due to scattering of light by the
particles of the dispersed phase ( which are
colloids). |
| Q.10. |
Write any one characteristic feature of
enzymatic catalysts.
|
| Ans. |
Enzyme catalysts are highly
specific in their action on substrate molecules
and each enzyme catalyses only a specific type
of reaction.
|
| Q.11. |
Account for the following
: (i) Silicone is
an insulator but silicon doped with phospphorus
acts as a semi - conductor.
(ii)
Some of the glass objects recovered from ancient
monuments look milky instead of being
transparent.
|
| Ans. |
(i) In pure silicon all its
four valencies are used up in producing diamond
like structure. When silicon is doped with
phosphorous ( with five electrons in its valence
shell). Out of these 5 electron four from bonds
and the fifth electron can convey electric
current readily. Hence, silicon doped with
phosphorus acts as a semi-conductor.
(ii) some of the glass
objects from ancient monuments look milky
instead of being transparent because of some
crystallisation occurring after a long exposure
to the atmosphere. They become a bit opaque.
|
| Q.12. |
Give
one example each of miscible liquid pairs
showing positive and negative deviations from
Raoult's law. Give one reason each for such
deviations.
|
| Ans.
|
Non - ideal solutions do not
obey Raolt's law. In them the solute-solvent
intermolecular forces are either weaker or
stronger than solvent-solvent intermolecuilar
forces. Example solution of cyclohexane in
ethanol. The solution of cyclohexane
in ethanol shows positive deviation from
Raoult's law. Ethanol molecules are associated
through hydrogen bonds. On adding cyclohexane
some hydrogen bonds break. The intermolecular
forces cyclohexane - ethanol become weaker than
ethanol - ethanol
intractions. The boiling
point of the solutions is less than the boiling
point of ethanol alone. Vapour pressure of this
solution is more than the vapour pressure of
pure ethanol.
The solution of acetone and
chloroform is an example of negative deviation
from Raoult law. There are no hydrogen bonds in
between chloroform - chloroform or between
acetone - acetone molecules but when they form
solution hydrogen bonding takes place as shown.
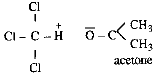
Due to this intermolecular
forces acetone - chloroform are stronger than
chloroform -chloroform- or acetone - acetone
intermoleculr forces. Solution boils at higher
temperature than the b.p. of the solvent and
vapour pressure of the solution is less than the
vapour pressure of pure solvent.
|
| Q.13. |
Starting with
the thermodynamic relationships
DE = q - PDV and H = E + PV derive the
relationship DH =
Qp* |
| Ans. |
H =
E + PV For
final stage H2
=E2+PV@ AND FOR
INITIAL STAGE H1
= E1
+PV,
Substracting H2 - H1
= (E2 + PV2) - (E2 + PV1)
or
H2 - H1 = DH = (E2-E1) +P (V2-V1)
or
DH = DE = PDV .....(1)
Also
DE + PDV = q-PDV
or
DE + PDV = qp
From
(1) and (2) DH = qp
|
| Q.14. |
From the data
given below at 298 K for the reaction :
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) --CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
Calculate the
enthalpy of formation of CH4 (g) at 298 K.
Enthalpy of
reaction = -890.5 kJ
Enthalpy of
formation of CO2
(g) = -393.5 kJ mol-1
Enthalpy of
formation of H2O(1) =-286.0 kJ mol-1
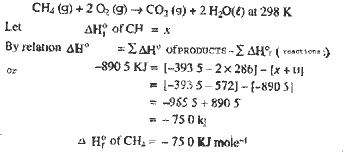
|
| Ans. |
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) --CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) at 298
K. |
| Q.15. |
Give the IUPAC
name of :
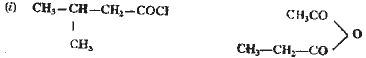
|
| Ans. |

|
| Q.16. |
Give explanation for the
following observations :
(I)
An ether would possess a dipole moment even if
the alkyl groups present in it are identical.
(ii)
Towards nucleophilic reagents aldehydes are more
reactive than ketones.
|
| Ans. |
(a) In any ether R--O--R the
bond angle R--O--r is 1100 due to the presence of two Ione
pairs on central oxygen atom. Therefore, ether R--O--R will have dipole
moment even if alkyl groups are identical.
 is not
linear. is not
linear.
(b)

|
| Q.17. |
For
the following conversion reactions write the
chemical equations : (i) Ethyl
isocyanide to ethylamine
(ii) Aniline to
N-phenylethanamide
|
| Ans. |
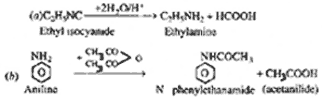
|
| Q.18. |
Account for the
following :
(i)
ammonolysis of alkyl halides does not give a
coresponding amine in pure state.
(ii)
If --No2 or ---
COOH group is attached to a carbon of benezene
ring, electrophilic substitution becomes
difficult.
|
| Ans. |
(a) The reaction of ammonia
with alkyl halides called ammonia alysis
produces a mixture of primary, secondary and
tertiary amines. Since this mixture of amines
cannot be separated easily. We cannot get pure
amines by ammonialysis
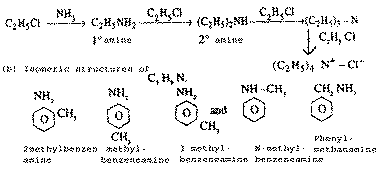
(b) If NO2 or --COOH group is attached to the
carbon atom of benzene ring, the benzene ring is
deactivated by reasonance as follows :
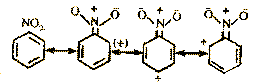
In these structures there is
+ve charge in ortho and para positions.
Therefore, they are unreactive to the attacking
electrophile which is positively charged.
Electrophilic substitution becomes difficult.
|
| Q.19. |
The
sums of first and second ionization energies and
those of third and fourth ionization energies of
nickel and platinum are given below : -
formula to be
inserted : |
|
IE1 + IE2 (MJ mol-1) |
EE3 + IE4 (MJ mol-1) |
|
Ni |
2.49 |
8.80 |
|
Pt |
2.66 |
6.70 |
|
taking these values into
account write :
(i)
The most common oxidation state for Ni and Pt
and its reasons.
(ii)
The name of the metal (Ni or Pt) which can form
compounds in +4 oxidation state more easily and
why. |
| Ans. |
Ans. to be
inserted. |
| Q.20. |
(a) Of the ions Ag+, Co2+, and Ti4+, which ones will be coloured in
aqueous solution. (Atomic nos. : Ag = 47, Co =
27, Ti = 22)
(b)
If reach one of the above ionic species is in
turn placed in a magnetic field, how will it
respond and why ?
|
| Ans. |
a) AG+ (4d10 5s0) and Ti4+ (3d0 4s0)
have no unpaired electrons but CO2+ (3d7 4s0) has three unpaired electrons.
Hence only CO2+
will be coloured in acqueous solutions. Others
Ag+ and Ti4+ will be colourless.
(b)
Out nof Ag+
(4d10 s0) Co2+ (3d74s0) and Ti4+ (3d0s0)
only CO2+ has
three unpaired electrons. When placed in a
magnetic field CO2+ will be attracted because it is
paramagnetic. Other ionic species Ag+, Ti4+ have no unpaired electrons. They
are diamagnetic. They will be fecbly repelled by
the magnetic field.
|
| Q.21. |
Among ionic species, Sc3+, Ce4+ and Eu2+, which one is a
good oxidising agent ? give a suitable reason
for your answer. ( Atomic nos. Sc = 21, Ce = 58,
Eu = 63). |
| Ans. |
Among Se3+ (3d0 4S0) Ce4+ (4f0 5d0
6s0) and Eu2+ (4f0 5d0 6s0) only Ce4+ is a good oxidising agent because
C4+ has a strong
tendency to revert to the more stable oxidation
state of +3 by gaining one electron Ce4+ + e- -- Cl3+. Eu2+ is reducing
agent. Eu2+ --
Eu3+ + 1e-1.
less
stable stable
state state
|
| Q.22. |
Explain the following
processes with a suitable example in each case :
(i) Chain -
growth polymerization
(ii) Step -
growth polymerization
|
| Ans. |
In chain growth
polymerisation an organic perioxide is used as
initiator and the monomers are added to the
freeradical in chain fashion. The polymer chain
is grown by adding small quantities of indicator
to produce reactive free radicals and adding
monomers at each addition of initiator.
In step growth
polymerization the condensation polymer like
backelite is produced from phenol and
formaldehyde by condensation reaction step by
step with or without elimination of smaller
molecules. The polymer chain is grown step by
step.
Nylon 66 is synthesised by
the condensation of hexamethyline diamine and
adipicacid. this produces polymamide linkages
with elimination of water molecule in each step.
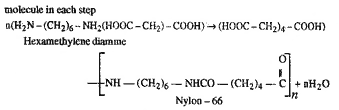
|
| Q.23. |
Giving an example of each, differentiate
between multimolecular and macromolecular
colloids.
|
| Ans. |
Multimolecular - the colloidal
particles of these colloidal solutions consist
of aggregates of atmosor small molecules with
diameter less than 1 nm. Example gold sol
consists of particles of various sizes having
several atoms. The atoms are held together by
weak Vander Waal forces.
Macromolecular Colloids - In
macromolecular colloids the dispersed particles
are themselves large molecules called
macromolecules of more than 1 nm diameter. They
have high molecular masses (1000 to 106). Naturally
occurring macromolecules are starch, cellulose,
gum and protein. |
| Q.24. |
What
arepolysachharides? Name one of them. How is it
important for us ?
|
| Ans. |
Polysachharides are formed
when large number of monosachharide molecules
get condensed with elimination of H2O molecules.
Example cellolose and starch. Starch is a food
reserve in plants. On hydrolysis starch forms
maltose. One further hydrolysis maltose forms
glucose. Glucose is a chief source of energy in
living systems as its oxidation in the body
provides 38 molecules of A.T.P.
|
| Q.25. |
What
do you understand by the statement : "ATP
molecules are the currency of energy metabolism
in a cell."
|
| Ans. |
Structure of A.T.P.
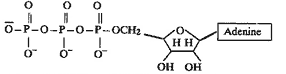
A.T.P. is an energy source
in human system. The molecule has four negative
oxygen atoms. Due to the repulsion of these
oxygen atoms ATP hreases readily and repulsive
forces are reduced.
ATP
-----------> ADP + P(D G <
0)
ADP
-----------> AMP + P(D G < 0)
Hydrolysis of ATP releases a large amount
of energy required for the human system.
|
| Q.26. |
Name
a broad spectrum antibiotic and state two
diseases for which it is prescribed.
|
| Ans. |
Chloramphenicol is a broad
spectrum antibiotic. It can be used for the
treatment of disentry, typhoid and urinary
infections. |
| Q.27. |
The
ionization energy of hydrogen atom in ground
state is 1312 kJ mol-1. Calculate the wavelength of
radiation emitted when the electron in this atom
makes a transition from n = 2 state to n = 1
state. [ Planck constant, h = 6.63 X 10-34 Js, velocity of
light, c=3X1010
cm S-1 and
Avogadro's number, NA = 6.02X1023 mol-1) |
| Ans. |
Ionisation energy of hydrogen = 1312 kJ
mol-1 Energy of electron in hydrogen (En) = -1312/n2 kJ
mol-1
E2 (energy
in x = 2) = -1312/ (2)2 = -328 kJ mol-1
E1 (in n =
1) = -1312 / (1)2
= -1312 kJ mol-1
DE = Energy emitted in transition form n = 2
to n =1
=
-328 - (-1312) = 984 kJ mol-1
Also
E = hc /l or l
= hc/E
Wavelength of radiation emitted =
(l)
=
6.6 x 10-34 x 3
x108 / 984 x1000
x 6.02 x 1023
l = 6.6 x 10-34 x 3 x 108 x 6.02 x 1023 / 984 x 1000 metre x 1/10-10
=
1207 A0
|
| Q.28. |
On
dissolving 3.24 of sulphur in 40 g. of benzene
boiling point of solution was higher than that
of benzene by 0.81 K. K1 value for benzene is
2.53 K kg. mol-1.
What is the molecular formula of sulphur?
(Atomic mass of sulphur = 32 g mol-1).
|
| Ans. |
Wt. of sulphur (WB) = 3.24 g
Wt. of benzene
(WA) = 40
g
DTb = 0.81 K
Kb = 2.53 K kg mol-1
Molecular mass
of Sulphur = Kh /
DTb x WB/ WA X 1000
= 2.53 / 0.81 x
3.24/40 x 1000
= 253 g mol-1
The no. of
atoms of sulphur in its molecule = 253 / 32 =
7.9
= 8 approx.
Molecular
formula of Sulphur is S8.
|
| Q.29. |
Calculate the
cell emf and DG for
the cell reactionat 250 C for the cell.
Zn(s) | Zn2+
(0.0004 M) || Cd2+ (0.2 M) | CD (s)
E0 values at
250C : Zn2+ / Zn = - 0.763V ;
Cd2+/Cd = - 0.403
V ;
F =
96500 C mol-1 ; R
= 8.314 JK-1
mol-1. |
| Ans.
|
For the cell Zn(s) | Zn2+ (0.0004 M) || Cd2+ (0.2M) | Cd (s)
The cell reaction is Zn(s) + Cd2+ (aq) --Zn2+ (aq) = Cd(s).
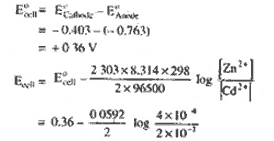
= -
0.36 - 0.0296 log 2 x 10-3
=
0.36 - (0.0296) x [ 0.2010 - 3]
=
0.36 - (0.0296) x (-2.6990)
=
0.44 V
D G = -n FE0
= -2x 96500 x 0.36
=
69.48 kj
answer to be inserted.
|
| Q.30. |
In
general it is observed that the rate of a
chemical reaction doubles with every 100 rise in temperature.
If this generalization holds for a reaction in
the temperature range 295 K to 305 K, what would
be the value of activation energy for this
reaction ? ( R = 8.314 K K-1 mol-1).
|
| Ans. |
T1 = 295 K
T2 = 305
K
K2 / K1 = 2 ( rate of
reaction doubles)
By the relation log K2 / K1
= EAC / 2.303 x R
x [ 1/T1 -
1/T2]
or,
EAC ( activation
energy ) = log K2
/ K1 x 2.303 x R
X T2 x T1 / T2 - T1
=
log 2 x 2.303 x 8.314 x 305 x 295 / 10
=
0.3010 x 2.303 x 8.314 x 305 x 295 / 10
=
5139998.255 Joule
|
| Q.31. |
Describe the
following :
(i) Optical
isomerism
(ii) Magnetic
behaviour of [ Ni (CN)4]2 -
ion. ( At. no. of Ni = 28)
(iii)
Preparation of tetrabutyl tin.
|
| Ans. |
(i) Optical isomerism in
Co-ordination compounds is exhibited when the
given compounds possesses no plane of symmetry.
The two isomers are mirror image of each other
and they rotate the plane of polarished light in
opposite directions. It is found that octahedral
complexes having bidentate ligands NH2--CH2--CH2--NH2
and oxalate COO - ion exhibit optical isomerism.
E.g. Co (en)3 has
two optical isomers.
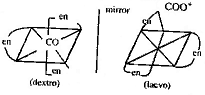
(ii)
[Ni (CN)4]2- . Oxidation state of Ni is =2 in
this complex.
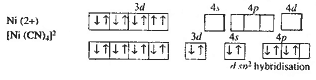
There is no unpaired electron in [Ni
(CN)4}@_ ION HENCE [Ni (CN)4]2- is diamagnetic.
(iii) Preparation of tetrabutyl tin
SnCl4 + 4 Bu Li -- Bu4 Sn = 4 LiCl)
(
Tetrabutyl tin) |
| Q.32. |
(a)
What is a nuclear fission reaction ?
(b) Describe
the basic principle of a nuclear reactor.
|
| Ans. |
(a) In Nuclear fission a
heavier nucleous like 235/92 U breaks into a
number of fragments by suitable bombardment with
slow neutrons. It is a chain reaction because
neutrons produced strike more particles of
235/92 U again and again Example : 235/92 u +
1/0 n ----- 139/56 Ba + 93/36 Kr + 3 1/0 n
(b) Principle of nuclear
reactor : In a nuclear reactor fission reaction
is made to take place under controlled
conditions. Energy released is used for the
production of electricity. In order to make the
speed of neutrons slow a moderator ( graphite or
heavy water) is used. Control rods made up of
boron, steel or cadmium are used to capture some
of the neutrons so that chain reaction does not
become violent.
|
| Q.33. |
(a)
Write chemical equations and reaction conditions
for the conversion of : (i) Propene to
1-bromo-propane.
(ii)
Chlorobenzene to phenol.
(iii)
2-proppanol to iodoform.
(b) How is
glyeerol obtained commercially. State its two
uses.
|
| Ans.
|
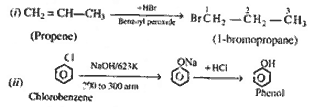
Uses of glycerol : (i)
glycerol is used as a sweetening agent in
medicines like cough syrup.
(ii) It is used in making
cosmetics because glycerol has the property of
retaining moisture.
|
| Q.34. |
(a) Account for
the following observations :
(i)
In several chemical properties lithium resembles
magnesium.
(ii)
+ 1 oxidation state of thallium ( atomic no. 81)
is more stable than its + 3 oxidation state.
(iii) Boron chloride exists as a monomer
while in the same group anhydrous aluminium
chloride exists as a dimmer.
(b)
Complete and balance the following chemical
equations :
(i) NH3 -- NaOCI --
(ii) XeF4 + SbF5 --
|
| Ans. |
(i) Important functions of
nucleic acids are : (a) REPLICATION : DNA has
double strand helical structure. It unwinds
itself and each strand synthesises its
complimentory template so that two new molecules
of DNA closely resem,bling the parent molecule
are produced.
(b) PROTEIN SYNTHESIS :
involves two steps (a) Transcription in which
DNA synthesises m-RNa which have base sequence
complimentary to base sequence in
DNA.
(c) TRANSLATION : iN WHICH
M-RNA provides code corresponding to base
triplelt on its nucleotide sequence to t-RNA
which carries the specific amino acid to the
site of protein synthesis. r-RNA attaches the
amino acids in the sequence provided by t-RNA.
(ii) Thailium (6s26P1) has + 1 stable state because of
Inert pair effect. Two electrons in 6s-orbital
do not take part in bond formation. This pair
remains inert. Hence Thallium has + 1 oxidation
state more stable than + 3 oxidation state.
(iii) The small size boron
atom cannot accommodate four large sized Cl ions
and B cl3 exists
as monomeric unit. In the case of larger sized
Aluminum atom used its vacent P-orbial in its
valence shell to complete its octet by forming
dimer. Hence, AlCl3 forms dimer in anhydrous state.
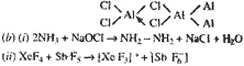
|