|
CBSE ANNUAL PAPER - 2000
BIOLOGY
(SET-I)
Time Allowed : 3
Hours
Max.Marks :
70
General
Instructions :
(i) All
questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question are indicated
against it.
(iii) Q. Nos. 1-11 are very
short answer type carrying one mark each only.
Answer them in one word one sentence.
(iv) Q. Nos. 12-23 are
short answer questions carrying 2 marks each. It
is appropriate to answer them in about 30-50
words.
(v) Q. Nos. 24-28 are short
answer questions carrying 3 marks each. It is
appropriate to answer them in about 30-50
words,.
(vi) Q. Nos. 29-32 are long
answer questions carrying 5 marks each. It is
appropriate to answer them in about 40-100
words.
(viii) Do not unnecessarily
make the answer lengthier than desired.
|
|
Section - A
Q. Nos. 1-8 are of very short answer type
carrying 1 mark each. Answer them in one word/
one sentence having 1 - 20 words each.
|
| Q.1. |
What is meant by trisomic condition ?
|
| Ans. |
It is a condition in which
three chromosomes of a particular type exist
together.
|
| Q.2. |
State the presence or absence of sinus
venous in a fish and a mammal.
|
| Ans. |
Fish - sinus
venous present. Mammal - sinus venous absent.
|
| Q.3. |
Which type of cartilage is present between
vertebrae to allow limited movement ?
|
| Ans. |
Hyaline
cartilage
|
| Q.4. |
Name any two breeds of wild rock pigeon
that have been developed through artificial
selection.
|
| Ans. |
Jacobin,
Pouter.
|
| Q.5. |
Which chromosomes are
called autosomes ?
|
| Ans. |
Somatic
chromosomes are called autosomes.
|
| Q.6. |
When is tumour referred to
as malignant ?
|
| Ans. |
Tumour is called malignant
when it spreads to distant places.
|
| Q.7. |
What are the two factors that contribute
for the disassociation of oxyhaemoglobin in the
arterial blood to release molecular oxygen in an
active tissue ?
|
| Ans. |
(i) Lack of ATP,(ii) Lack
of Oxygen. |
| Q.8. |
Which one of the following is fatal unless
oral rehydration therapy is administered: (i)
Whooping cough, (ii) Cholera, (iii)
Tetanus |
| Ans. |
Cholera |
|
Section -
B
Q. 9-18 are of short answer
type carrying 2 marks each. Answer them in
approximately 20-30 words
each.
|
| Q.9. |
What are the two functions
of DNA polymerase ?
|
| Ans. |
The two
functions of DNA polymerase are -
(i) To synthesize new DNA strand in 5 - 3
direction.
(ii) To do proof reading and DNA repair.
|
| Q.10. |
Stanley Miller and Harold C. Urey
performed an experiment by recreating in the
laboratory the probable conditions of the
atmosphere of the primitive earth.
(i) What was
the purpose of the experiment ?
(ii) In what forms was the energy supplied
for the chemical reactions to occur ?
(iii) For how
long the experiment was run continuously ?
|
| Ans. |
(i) To show
that life originated from inanimate.
(ii) Electrodes.
(iii) A week.
|
| Q.11. |
How does the mustard inflorescence differ
from the banana inflorescence in arrangement ?
Give the technical term for each.
|
| Ans. |
Mustard
Inflorescence |
Banana
Inflorescence |
|
(i) It is called Raceme.
|
(i) It is called
spadix. |
|
(ii)Flowers are borned
in
acropetal succession
and are
pedicallate. |
(ii)Flowers one borne
in
acropetal succession
but are sessile.
|
| Q.12. |
Name the basic nitrogenous catabolite of
proteins produced in birds. In what form is it
is eliminated from their body ? What is the
advantage of this type of excretion ?
|
| Ans. |
The basic nitrogenous
catabolite of proteins produced in birds is uric
acid. It is eliminated from their body in the
form of solid. This type of excretion is useful
to conserve water.
|
| Q.13. |
Describe the theory of inheritance of
acquired character. Who disproved it
experimentally ?
|
| Ans. |
Jean Baptist de Lamarck
gave the theory of inheritance of acquired
characters. It has three main features -
1. The effect of
environment : The
environment changes the organism for its better
adaptation.
2. Use and disuse of body parts :
When the organism adapts itself for a new
environment the organs that are more in use are
changed and this change is seen in the next
generations.
3. Inheritance of acquired
characters : When these changes are
regularly inherited to the next generations the
organism represents a new species.
Weismann disproved this
theory. He showed that even after cutting the
tail of the rats for several generations, no rat
was born without a tail. This means that disuse
of tail did not lead to loss of the tail in the
offsprings.
|
| Q.14. |
Differentiate between morula and blastula
of mammals.
|
| Ans.
|
Morula
|
Blastula
|
|
(i) It is 16-32 celled
structure. |
(i) It is 32-64 celled
structure. |
|
(ii) It is solid.
|
(ii) It is
hollow. |
|
(iii) It doesn't have
cavity. |
(iii) It has cavity
blastocoel. |
| Q.15. |
What is the biological significance of
Azolla pinnate in agriculture ?
|
| Ans.
|
The biological significance
of Azolla pinnate in agriculture is that it
helps in nitrogen fixation and increases the
field of rice crop.
|
| Q.16. |
Give any two reasons to justify that
ginger is a modified stem.
|
| Ans. |
The two reasons that
justify that ginger is a modified stem are -
(i) It bears nodes and internodes.
(ii) It bears scaly
leaves. |
| Q.17. |
Define biogeography. How do Darwin's
Finches provide the biogeographical evidence in
favour of evolution
? |
| Ans. |
Biogeography is the study
of distribution of animals and plants in the
world. Darwin's finches were found on Golapagos
islands. They differ in size and beak shape as
they adapted themselves according to the
available food in that island.
|
| Q.18. |
Explain the structural and functional
significance of fovea in the human eye.
|
| Ans. |
The structural and
functional significance of fovea in human eye is
(i) Fovea consists of cones only.
(ii) It is used to focus a particular
object.
|
|
Section -
C
Q.
Nos. 19-27 are of short answer type carrying 3
marks each. Answer them in approximately in
30-50 words each.
|
| Q.19. |
What is meant by R cells and S cells with
which Frederick Griffith carried out his
experiments on Diplococus pneumoniae ? What did
he prove from these experiments.
|
| Ans. |
In 1928, an English
bacteriologist, Fredrick Griffth conducted
experiments with the bacterium that causes
pneumonia, Diplococcus Pneumonia. There are two
main types of this bacteria, smooth (S) and
rough (R) S-S-type cells have a capsule around
capsule, are virulent and cause pneumonia. The
R-type bacteria do not have the capsule and are
avirulent and harmless. The S-type bacteria when
injected into mice cause pneumonia and
subsequent death of the animal whereas the
R-type bacteria when injected into mice and
found to be harmless. Griffith found that the
S-type bacteria when killed by heat prior to
injection into mice did not cause the disease.
However, when heat killed S-type bacteria were
injected into mice along with avirulent, R-type
bacteria, mice suffered from pneumonia and died.
Examination of the dead mice revealed the death
occurred due to the living S-type bacteria.
Griffith concluded from this experiment that the
avirulent R-type bacteria had been transformed
into S-type, capsule variety. In other words,
the dead S-type bacteria had transmitted their
virulence to the living R-type avirulent
bacteria. This experiment showed the some
component of the bacterial cell is responsible
for the phenomenon of transformation.
|
| Q.20. |
Draw a diagram of T.S. of a part of
somniferous tubule of testis of an adult human
male and label any six parts in it.
|
| Ans.
|
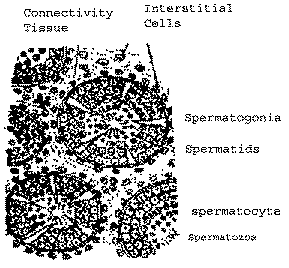
|
| Q.21. |
How does industrial melanism bring out the
action of natural selection ?
|
| Ans.
|
Biston betularia (Peppered
moth) exists in two strains white ( dull grey)
and black. It was found on tree trunks in
England in abundance before industrial
revolution. As the tree - barks were covered by
whitish lichens thus white moths were able to
hide them from predating birds.
But with industrialisation,
barks of trees got covered by black sooth of
smoke and converted to blackish colour as a
result white moths were easily identified by
predator birds. But black moths (just 10 % of
total ) could escape themselves slowly and
gradually through hundred of years, black
coloured moths ( carbonaria) increased to 90%
and white moths decreased.
Gradual replacement of coal
by oil and electricity and measures to control
soot formation, the trees recovered and become
lighter in shade hence again population of white
moths increased. It showed and proved how nature
has played its role in deciding the type of
population to exist according to their adaption
towards the environment.
|
| Q.22. |
How does intestinal juice contribute in
the digestion of proteins ? What provides
alkaline pH in the small intestine ?
|
| Ans. |
1. Entero peptidase - It activates
pancreatic trypsinogen to trypsin and trypsin
breaks proteins into peptides.
2. Amino
peptidases - It separates amino acids
from peptides.
3. Di peptidases - They hydrolyse
dipetides into amino acids. Alkaline medium is
provided by brunner's glands in the intestines.
|
| Q.23. |
An
RNA strand has a series of condoms out of which
three are mentioned below :(i) AUG (ii) UUU and
(iii) UAG. (a) What will
these condoms be translated into ?
(b) What are the DNA condons that would
have transcribed these RNA condons ?
|
| Ans. |
(a) (i) AUG -
Methionine (ii) UUU - pheny alanine
(iii) UAG - Nonsense condon
(b) (i) AUG - TAC
(ii) UUU - AAA
(iii) UAG - ATC
|
| Q.24. |
List any four symptoms shown by a Down's
syndrome afflicted child. Explain the cause of
this disorder.
|
| Ans.
|
For symptoms
of Down's Syndrome are - 1.
Rounded face
2.
Broad forehead
3.
Flatened nasal bridge
4.
Open mouth
It
oooccurs due to trisomy of 21st Chromosome.
|
| Q.25. |
Answer the following with reference to the
anatomy of dicot stem :
(i) Where exactly are the cambial cells
located in the vascular bundles ?
(ii) What is
the name given to such a bundle ?
(iii) How are the exylem vessels arranged
?
(iv) What type
of cells constitute the pith ?
|
| Ans. |
(i) In between
xylem and phloem cells. (ii) Collateral and
open.
(iii) Endarch
conditions.
(iv) Parenchyma.
|
| Q.26. |
Explain any three chemical barriers that
offer non-specific defence mechanism.
|
| Ans. |
Three chemicals barriers
that offer non-specific defence mechanism are -
(i) Sweat (ii) Sebum (iii) Lysozyme.
|
| Q.27. |
Trace the development of microsporocyte in
the anther to a mature pollen - grain.
|
| Ans. |
Anther consists of four
anther sacs. Anther sac is made up of
sporogenous tissue. It consists of cytoplasmic
cells. The cells divide mitotically and forms
microspore mother cells. Each microspore mother
cell undergoes meiosis to form four haploid
microspore. The four microspore formed
from a microspore mother cell are arranged in a
tetrahedral form. Each microspore or pollen
grain has two layers, an outer thick exine and
an inner thin intine. The pollen grain divides
to form a generative cell and a vegetative cell.
The generative cell give rise to two male
gametes and a vegetative cellforms pollen tube
nucleus that direct pollen tube towards
micropyle for fertilization.
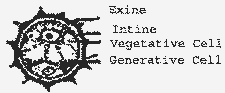
|
|
Section - D
Q.
Nos. 28-30 are long answer types carrying 5
marks each. Answer them in approximately 80-120
word each.
|
| Q.28. |
In
the case of snapdragon ( Antirrhinum majus) a
plant with red flowers was crossed with another
plant with white flowers. Trace the inheritance
of flower colour up to the F2 generation indicating the
genotypes and phenotypes at each level. What
special feature do you note in the genotypic and
phenotypic ratios in F2 generation
? |
| Ans. |
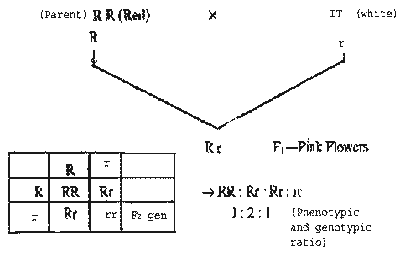
|
| Q.29. |
Name the hormone that regulates each of
the following and mention the source of it :
(i) Urinary
elimination of water
(ii) Storage
of glucose as glycogen
(iii) Sodium
and potassium ion metabolism.
(iv) basal
metabolic rate
(v) Descent of
testes into the scrotum
|
| Ans. |
(i) ADH |
Posterior pituitary
|
|
(ii) Insulin
|
Pancreas |
|
(iii) Minero corticoid
|
Adrenal gland
|
|
(iv) T3 and T4
|
Thyroid
|
|
(v) Tetosterone
|
Testes |
| Q.30. |
Describe the C4 pathway in a paddy plant. How is
this pathway an adaptive advantage to the plant
?
|
| Ans.
|
The anatomy of leaves of
C4
plants is
different from leaves on C3 plants. This type of anotomy is
called Kranz anatomy. In the leaves of such
Plants, Palisade tissue is absent. There is
bundle sheath around the vascular bundles. The
chloroplasts in the bundle sheath cells present
are large and without or less developed groove
whereas in the mesophyll cells the chloroplasts
are small but with well developed groove.
CO2 taken from atmosphere is accepted
by a 3 carbon compound. Pyruvate in the
chloroplasts of mesophyll cells leading to the
formation of 4-C Compound oxaloacelate converted
to another 4-C Compound the malic acid. It is
transported to the chloroplasts of bundle sheath
cells. Here malic acid (C4) is converted to Pyruvic acid
(C3) with the
release of CO2.
Thus concentration of CO2 increases in the bundle sheath
cells. These cells contain enzymes of Calvin
cycle. Because of high concentration of CO2, RuBP Carboxylase
participate in Calvin cycle and not in
photorespiration . Sugar formed in Calvin cycle
is transported into the phloem.
Pyretic acid generated in
the bundle sheath cells re-enters mesophyll
cells and regenerates phosphoenol pyruvic acid
by consuming one ATP.
Since the conversion
results in the formation of AMP ( not ADP),
needs 12 glucose molecule, wheres C4
Pathway requires 30
ATP.
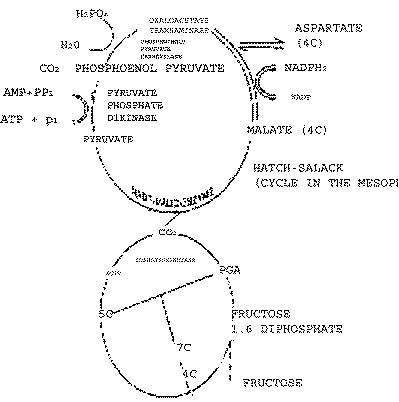
|