|
CBSE ANNUAL PAPER - 1998
SCIENCE
(THEORY)
(SET-I)
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 75
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question are indicated against it.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to 10 are very short answer type questions, carrying 1 mark each to be answered in one word or maximum in one sentence.
(iv) Question numbers 11 to 20 are short answer type questions. Carrying 2 marks. answer may not normally exceed 40 words each.
(v) Question numbers 21 to 30 are short answer type questions of 3 marks each. Answer may not normally exceed 60 words each.
(vi) Questions numbers 31 to 33 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each, which should not be answered in more than 100 words each.
(vii) Please write down the serial number of the question before attempting it.
|
| Q. 1. |
Name the device
which directly converts solar energy into
electrical energy. |
| Ans. |
Solar Cell |
| Q. 2. |
Name the technique
of collecting information through a satellite
about an object from a distance.
|
| Ans. |
Remote sensing.
|
| Q. 3. |
An engine supplies
12,000 joule of energy per minute. How much
power is supplied by it ? |
| Ans. |
Energy supplied - 12,000 J Time - 1 min. = 60
sec.
Power = Energy /
Time
= 12,000/60 = 200
watt. |
| Q. 4. |
Lights from two
different sources A and B have wave lengths 0.3
micron and 0.7 micron respectively. Which one of
the two lights carries more energy per photon ?
|
| Ans. |
Light from source A carries more energy
per photon as its wave Length is smaller.
|
| Q. 5. |
Name any two gases
whose presence in air causes green-house effect.
|
| Ans. |
CO2, O3 and vapours.
|
| Q. 6. |
Name the main
constituents of common brass.
|
| Ans. |
Copper (Cu) and Zinc
(Zn). |
| Q. 7. |
Which properly of
diamond gives its special shine ?
|
| Ans. |
Diamond is transparent with high
refractive Index and it possesses excellent
cleavage along many intersecting planes which
can be polished. All these three properties make
it special shining substance. |
| Q. 8. |
Boiled milk does
not spoil quickly. Why ?
|
| Ans. |
The micro-organisms responsible for the
spoilage of milk are destroyed on boiling, hence
it does not spoil quickly. |
| Q. 9. |
Which one of the
following in a food chain will have maximum
concentration of harmful chemicals in its body :
Small fish, Zooplankton, Birds,
Phytoplankton. |
| Ans. |
Food chain :
Phytoplankton --
Zooplankton -- Small fish Birds.
As birds are at the
top of the food chain, so, birds will have the
maximum concentration of the harmful chemical in
their body.
|
| Q.10. |
A farmer grows
rice crop year after year in his field. He
notices a gradual decrease in yield. What could
be its cause ? |
| Ans. |
Gradual decrease in yield is noticed by
farmer due to depletion of nutrients,
particularly nitrogen, in the field caused by
monoculture i.e. growing the same crop (rice) in
the same field year after year. Field becomes
depleted of certain nutrients which decreases
yield.
|
| Q.11. |
Name the full
gases formed when (i) steamand (ii) a restricted
amount of air are passed through a bed of red
hot coke. Write the names of their combustible
components :
|
| Ans. |
(i) When steam is passed over red hot
coke, water gas is produced which is a mixture
of CO and H2
gases
C +
H2O --------- CO
+ H2
Red Hot Steam Water gas
Coke
Both the components
of water gas i.e. CO and H2 are combustible.
(ii) When restricted
amount of air is passed over red hot coke,
producer gas is produced which is a mixture of
CO and N2 gases.
C + AIR
---------- CO + H2
Red Hot Restricted amount
Producer gas
Coke
CO,
carbon monoxide of producer gas is the
combustible component. |
| Q.12. |
Calculate the
power of an engine which can lift 300 Kg. of
water through a vertical height of 15 m in 15
seconds. ( g = m/s2 ). |
| Ans. |
Solution : Amount of water (m) = 300 Kg.
Height (h) = 15
m.
Acceleration due to
gravity (g) = 10m/s2.
Energy required or
work done by engine = m x g x h.
= 300 x 10 x 15 J
= 45000 J
Power = work done /
time
Power of engine =
45000/15 = 3000 watt. ( 3 K. watt.)
|
| Q.13. |
Mention any two
differences between chemical and nuclear
reactions. |
| Ans. |
Chemical reactions
|
Nuclear
reactions |
|
(i)
Electrons of outer most orbit take part in a
chemical reaction while the nuclear particles -
protons and neutrons remain unaffected.
|
(i)
Nuclear particles - protons and neutrons take
part in a nuclear - reactions while the
electrons remain unaffected. |
|
(ii)
Amount of energy produced or absorbed in a
chemical reaction s is very very low as compared
to nuclear reaction. |
(ii)
Energy produced or absorbed in a nuclear
reactions is very high as compared to chemical
reaction. |
|
(iii)
New elements are not produced in a chemical
reaction. |
(iii)
New elements are produced by the result of
nuclear reaction. |
| Q.14. |
Kerosene burns in
a cooking stove to give a blue flame while it
gives a yellow flame when burnt in a lantern.
Give reasons for this difference.
|
| Ans. |
(i) Kerosene is burnt in a cooking - wick
stove or pressure stone with sufficient amount
of air, so it burns with a blue flame due to its
complete combustion. Wick stove possesses a
perforated sheet around the wicks. These
perforations allow the hot air to enter near the
wicks to aid in combustion while in a pressure
stove Kerosene coming out from the burner
strikes with hot burner and converts into
vapours. These vapours get sufficient air from
surrounding and complete combusion occurs with a
blue flame. (ii) In a lantern,
there is no provision for the free supply of
adequate oxygen ( or air ) for the complete
combustion of Kerosene in wick of lantern. Thus
Kerosene in a lantern burns in insufficient
oxygen ( or air ) which leads to incomplete
combustion and unburnt particles rise in flame.
These particles glow in hot flame and make the
flame luminous in yellow colour.
|
| Q.15. |
Give two
differences between a star and a shooting star.
|
| Ans. |
Star |
Shooting
Star |
|
1. It
is a heavenly body having its own light which
make it illuminated. |
1.
These are the heavenly bodies from sky which are
reflected from their path and are attracted
towards earth when they enter the atmosphere,
start to burn due to friction of air.
|
|
2.
Their mass is very much higher than a shooting
star and made up of mainly hydrogen and helium
gases. |
2.
Their mass is very less comparatively and are
made up of dust and solid bodies.
|
| Q.16. |
What is smog ?
Name any two diseases caused by smog.
|
| Ans. |
Smog : Smog is a mixture of smoke and fog.
During winter when smoke from industries,
vehicles or houses, mixes with the condensed
water vapours and dust particles, smog is
formed. Generally it is found in industrial
areas, big cities or over - crowded area. It is
the major problem of metropolitan areas. Smog
contains some harmful fumes also. Smog does not
go high into the atmosphere as a layer of warm
air is formed over the smog and cover it.
Name of diseases :
Smog causes bronchitis, Heart diseases, lung
cancer and some other respiratory diseases.
|
| Q.17. |
A trivalent metal
X is manufactured by the process of
electrolysis. It is the most abundant metal in
the earth's crust. Identify the metal and state
its two uses.
|
| Ans. |
X metal is trivalent, manufactured by
electrolysis and is abundant in earth crust; so
, it is Aluminum. Uses : (i) Aluminium
is used to make the electric wires for
conduction of electricity as it is good
conductor of electricity.
(ii) Door frames,
windows, handles, utensils and aircraft frames,
engine parts are made from aluminium.
|
| Q.18. |
What is meant by a
functional group in an organic compound ? Give
the structural formulae of the functional groups
in (i) Acetic acid and (ii) ethyl alcohol.
|
| Ans.
|
Functional
Group : A group of elements in organic
compounds when replaces hydrogen atom of
hydrocarbon, produces specific properties in the
compound and is known as functional group. e.g.
OH naming hydroxyl group produces alcoholic
properties while - COOH naming carboxyl group
produces acidic properties in the organic
compounds. (i) In Acetic acid (
CH3 COOH ) -
cooh, Carboxyl group is the functional group.
O
Structural formula :
- C - OH
(ii) In Ethyl
alcohol, OH, hydroxyl group is the functional
group.
Structural formula -
OH. |
| Q.19. |
What is sickle
cell anemia ? What is its direct effect ?
|
| Ans. |
Sickle Cell anaemia : Sickle cell anaemia
is a genetic disease which is transferred
generation to generation. It is caused by mutant
gene. In this disease RBC of the affected person
become sickle shaped instead of round and
haemoglobin becomes defective. Effects : Because of
defective haemoglobin, patient becomes deficient
of oxygen and following effects are seen :
(i) Headache and
dizzliness.
(ii) Cardiac and
pulmonary changes.
(iii) Nausea and
even death. |
| Q.20. |
Mention the
difference between the food habits of organisms
belonging to the first and third trophic levels.
Give one example of each of them.
|
| Ans. |
First trophic
level : Organisms at first tropic level are
the producers which contain chlorophyll and are
capable to manufacture their organic food from
in organic substances - CO2 and H2O in the presence of sunlight e.g.
Green lands. Third trophic level : Organisms at
third trophic level are the carnivores which are
not capable to manufacture their food like that
of green plants rather they get their food from
the herbivores in the form of flesh.
|
| Q.21. |
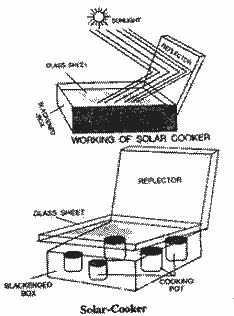
Describe the construction of a solar
cooker. How does it cause a rise in temperature
to cook food ? |
| Ans. |
Construction of a
solar cooker : (Box type ) : It consists a
blackened insulated box of wood or of a similar
material. Its upper open part is covered with a
glass sheet. The inner walls of the box are
painted black to maximum absorption of heat and
to minimise heat losses due to reflection. Glass
sheet allows to enter the considerable visible
light and infra-red rays from sunlight into the
box but do not allow to go out the radiated heat
from inner blackened walls and thus inner part
of the box gets sufficient temperature for
cooking the food. Inner part of lid of
the box is made good reflector and lid is so
attached with the box that it can be adjusted at
different angles to reflect the maximum sunlight
on the inner blackened walls of the box. Cooking
pots with food stuffs are placed in the box.
Rise in temperature : When a solar
cooker is placed in sunlight in such a way that
the sunlight falling on reflector enters the
blackened box through glass sheet. Its inner
surfaces become hot after absorbing solar
energy. As a result, these surfaces start
radiating heat in the form of infra red rays.
Glass sheet does not allow these rays to go out
as the wave length of these infra - red rays is
relatively longer. Thus temperature of the inner
part of the box rises upto 1000 - 1400 C which is sufficient to cook the
rice, pulses, meat etc.
|
| Q.22 |
What are rocket
propellants ? Mention any two of their important
characteristics. Give an example of liquid
propellants. |
| Ans. |
Rocket
Propellant : Special fuels that are highly
compact and burn rapidly and completely
producing a very large volume of gases per gram
weight leaving no dead weight of residue, are
called rocket propellants. Characteristics :
(i) They must burn rapidly and completely.
(ii) They should
produce a large volume of gases per gram weight.
(iii) They should
not leave dead weight residue.
(iv) They should be
compact.
Liquid Propellant :
Liquid hydrogen with liquid oxygen.
|
| Q.23. |
Name the process
involved in the liberation of energy in (i) the
sun and (ii) a nuclear reactor. Mention any two
differences between the two processes.
|
| Ans. |
In Sun : Energy is liberated by nuclear
fusion process in the sun. In Nuclear Reactor :
Nuclear fission is the process by which energy
is liberated in the nuclear reactor.
Differences :
|
|
(i)
Smaller nuclei fuse to form a big nucleus in
this process. e.g. Four hydrogen atoms fuse to
form the nucleus of helium. H H
+ --------------
He
H H |
(i) A
bigger nucleus splits up into two smaller nuclei
in this process. e.g. U-235 nuclear splits up
into Kr. and Banuclei when slow moving neutron
is bombarded on U-235 nucleus. |
|
(ii)
This process can not be performed in the
laboratory as it required very high temperature
to start. |
(ii) It
can be performed in the laboratory and can be
controlled. |
| Q.24. |
The mass of star A
one tenth that of star B. If the mass of A is
nearly equal to that of the sun, which one of
the two stars will end up as supernova ? What
would happen to the other star at the end of red
giant phase ?
|
| Ans. |
The mass of star A is 1/10th of the mass
of star B. The mass of star A is nearly equal to
the mass of the sun, so the mass of star B is
about ten times more than that of sun.
Therefore, star B will end up as supernova.
The other star A
having the mass equal to the mass of the sun
will end up as a white dwarf star. After the end
of red grant phase. Its outer shell. The core
left behind would gradually condense into an
extremely dense ball of matter. The resulting in
full temperature in its interior would then
begin the helium to fuse into higher elements
like carbon in the same way as the hydrogen was
fused into helium. The energy liberated by its
core make this core glow and a white dwarf star
as long as the helium lasts before ending into a
dense lump. |
| Q.25. |
Define Isomerism.
Write the structural formulae and the names of
the isomers of butane. |
| Ans. |
Isomerism : The property of compounds by
virtue of which compounds have the similar
molecular formula but different structural
formula, is known as isomerism. Isomers of butane :
H H H H H H H
| | | | | | |
H --
--C----C----C------C---H-----H--C------C---------C-----H
| | | | | | |
H H H H H | H
| | |
normal - Butane
H------C----------H
n - butane
|
(C4H10) H
Iso - Butane
(C4H10) |
| Q.26. |
Describe any three
ways in which the water important for the
activities of living beings.
|
| Ans. |
Importance of water in living beings :
(i) As solvent : Many substance are
required by the livings in the solution form
where water acts as solvent viz. digested food
is absorbed by the body in the solution farm.
(ii) As carrier : Water carries waste
products in the body to the excretory organs
from where they are excreted out from the body.
(iii) Regulates body temperature :
Water in the form of sweat evaporates and thus
regulates the body temperature during summer.
|
| Q.27. |
A cow is being fed
on straw, oil cake, oil-seeds, gram and bajra.
To what classes of feed to these items belong
and what is their importance ?
|
| Ans. |
(i) Straw belongs to the Roughage class of
feed which provides cellulose i.e. carbohydrate
to the body. It provides energy and raw material
for the formation of fats in the animal's body.
(ii) Oil cake, oil
seeds, gram and bajra belong to the concentrate
class of cattle feed.
They provide
proteins, vitamins and minerals to the animal.
It is energetic, it provides body building
material and regulates metabolic activities in
the body.
|
| Q.28 |
Moisture content
of four food items P, Q, R and S is 10 %, 15 %,
25 % and 50 % respectively. Which of these
require cold storage and which ones dry storage
? Give reasons.
|
| Ans. |
Cold Storage : Food items R and S
containing 25 % and 50 % moisture respectively
should be stored at low temperature i.e. these
two require cold storage as they have higher
moisture content than safe limit Higher moisture
can facilitate the micro-organisms to grow and
they spoil the food. At low temperature the
growth of microbes reduced and their action is
inhibited. Low temperature inhibits the
enzymatic action also. (i) Enzymes become
inactive.
(ii) Growth of
microbes is reduced.
(iii) Microbes
become inactive.
(iv) Infestation of
insects is also inhibited.
Dry storage : Food
items P and Q having low moisture i.e. 10 % and
15 % respectively, can be stored at room
temperature. Food items having 14 % moisture,
remain safe at room temperature as this moisture
content does not facilitate the microbes insects
and enzymes to be active and food does not
spoil. |
| Q.29. |
Name the
radiation's absorbed by the ozone layer. Give
any two causes of the depletion of ozone layer.
Name the disease likely to be caused due to its
depletion. |
| Ans. |
Ozone layer absorbs the ultra violet
Radiations coming from the sun. Causes of ozone depletion : (i)
Excessive use of 'Aerosol' chemicals like
chlorochloro carbon ( clcIC), chlorofloro carbon
(cl.F.C.) destroy the ozone layer.
(ii) Gases released
from the Rocket -exhaust also dissolve the ozone
layer and deplete it.
Disease : Depletion of ozone will
allow the ultra violet rays to reach the earth
surface where they will cause :
(i) Skin cancer
(ii) Damage to the
new cells
(iii) Gene mutation
resulting in genetic diseases in livings.
|
| Q.30. |
What is nitrogen
fixation ? Mention two points of difference
between nitrification and denitrification
processes. Name the organisms involved in these
processes.
|
| Ans. |
Nitrogen fixation : Green plants cannot
utilise the free atmospheric nitrogen for their
growth and food manufacturing. Some bacteria
like Rhizobium and some blue green algae are
capable to convert the free atmospheric nitrogen
into nitrate form, which can be readily utilized
by plants. This process of conversion of free
atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates is known as
nitrogen fixation. |
|
Nitrification
|
Denitrification
|
|
(i) The
fixed nitrogen is amonified by microbes i.e. it
is converted to ammonia. This ammonia is
converted by some other microbes into nitrite
and nitrates, it is know as nitrification.
(ii) It is oxidising
process.
Organisms :
* Ammonia to nitrite
- Nitrifying bacteria
( Nitrosomonas)
* Nitrite to Nitrate
- Nitrobactor |
(i) By
other kind of microbes nitrates are converted to
free nitrogen, it is known as denir-ification.
(ii) It is of
reduction type process.
Organisms
:
Nitrate to Nitrogen
- Pseudomonas ( Denitrificating bacteria)
|
| Q.31. |
Draw diagram of a
nuclear reactor. What is the role of moderators
in it? How are nuclear reactor used to generate
electricity ? |
| Ans. |
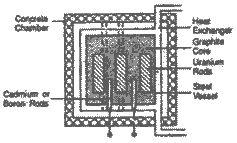
Role of
Moderators : Moderators like Graphite,
cadmium, boron etc. slow down the nuclear
fission reaction renders to control extent by
absorbing extra neutrons i.e. They avoid the
chain reaction.
Use of nuclear
reactor to generate electricity : As nuclear
reactor is fired the nuclear fission reaction
starts. Heat generated in the reactor is
withdrawn by circulating liquid sodium
continuously through pipes embodied in the
reactor. Liquid sodium becomes hot on gaining
heat from the reactor and gives to the water of
heat(-) exchanger when it passes through coiled
pipes embedded into the water of heat exchanger.
This heat generates steam. Super heated high
pressure steam is passed through turbine chamber
with the help of pumps. It drives the turbine.
Turbine rotates the generator by virtue of which
electricity is generated. The used steam
condenses and passed through a condenser to heat
exchanger back in the form of water for the
formation of new steam.
Here generation of
electricity is shown in the following diagram.
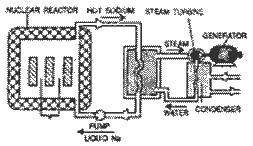
|
| Q.32. |
(i) Describe the
steps involved in manufacture of blister copper
from concentrated copper sulphide ore.
(ii) State the process of obtaining pure
copper from blister copper with the help of a
labelled diagram.
(iii) Name the elements which are mixed
with copper to prepare German silver.
|
| Ans. |
Following steps are involved in the
manufacture of blister copper from concentrated
copper sulphide ore : (i) Roasting : Concentrated ore is
roasted in the presence of air on a furnace i.e.
strongly heated inthe adequate quantity of air.
In roasting a part of CUS ( concentrated ore) is
converted into copper oxide (CuO) and other
volatile impurities which escape away in the
form of gases.
D
2CuS + 3O2 ------ 2 CuO +
2SO2
(ii) Reduction : After roasting CuO is
reduced to Cu either by using a reducing agent
viz. Coke or reduced by stopping air supply
during roasting following reactions occur.
D
2CuO + CuS ------ 3
Cu + SO2
D
2CuO + C ------ 2 Cu
+ CO2
(iii) Blister Copper : Copper
thus formed is in molten state. Since sulphur
dioxide gas passes though molten copper, sort of
blisters are developed on the surface of copper.
Similar situation arises during escape of CO2 through molten
copper. The pure copper is obtained by
electrorefining of blister copper.
(iv) Refining of blister copper : Blister
copper is refined by the electrolysis process. A
pure copper wire is made cathode and the rod of
impure blister copper is made anode. CuSO4
solution is taken as electrolyte in a
electrolytic cell. On passing electricity pure
copper is obtained deposited at cathode while
the impurities remain near anode. Timely, impure
blister copper rod is again inserted at anode to
get it be purified.
At
Anode : Cu - 2e = Cu++
At
Cathode : Cu++ +
2e = Cu

(iii) German silver :
German silver is an alloy of Cu, Ni and Zn. Thus
nickle and zinc are mixed with copper to obtain
German silver.
|
| Q.33. |
(i) Name the
elements that constitute proteins.
(ii) What are end products of protein
digestion and where are they absorbed ?
(iii) Name any three types of proteins
found in our body and mention their functions.
|
| Ans. |
(i) C,H,O and N are the main elements
which constitute the proteins. Besides these
elements S and P are also found in some of the
proteins.
Proteins are
digested by the action of proteinase enzymes
into amino acids. The digestion of proteins
occurs into stomach and small intestine while
the digested proteins i.e. amino acids are
absorbed by the small intestine.
(iii) There are many
types of proteins. Each type perform specific
functions like -
(a) Transport protein e.g. Haemoglobin.
Transport proteins transport some substances
from one part to the another part of the body.
Haemoglobin carries O2 from lungs to each and every part
of the body and carries CO2 back to the lungs from where it is
exhaled out from the body.
(b) Enzyme e.g. lipase. Enzymes are the
catalysts found in living cells which catalyse
specific chemical reactions in the body at body
temperature. for lipase catalyses the digestion
of fats into fatty acids.
(c) Protective Proteins e.g. Antibodies.
Antibodies are such proteins which protect the
body from diseases, thus immune the body.
|