|
CBSE ANNUAL PAPER - 2000
SCIENCE
(THEORY)
(SET-I)
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 75
General Instructions :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks for each question are indicated against it.
(iii) Question numbers 1 to 10 are very short answer type questions, carrying 1 mark each to be answered in one word or maximum in one sentence.
(iv) Question numbers 11 to 20 are short answer type questions. Carrying 2 marks. answer may not normally exceed 40 words each.
(v) Question numbers 21 to 30 are short answer type questions of 3 marks each. Answer may not normally exceed 60 words each.
(vi) Questions numbers 31 to 33 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each, which should not be answered in more than 100 words each.
(vii) Please write down the serial number of the question before attempting it.
|
| Q.1. |
Mention two harmful effects
of nuclear radiations on human body.
|
| Ans. |
(i) Nuclear radiations cause
irreparable damage to cells.
(ii) They cause gene
mutation which leads to chromosomal disorder for
many generations.
(iii) They cause cancer.
|
| Q.2. |
Name any two constellations
that are visible during winter in the northern
hemisphere. |
| Ans. |
(i) Pleids ( Krittika
)
(ii) Orion
|
| Q.3. |
Write an aquatic food chain.
|
| Ans.
|
Phytoplankton --- Zooplankton -- Fish ---
Kingfisher. |
| Q.4.
|
How does nuclear fuel of a
star differ from that of a white dwarf?
|
| Ans. |
Nuclear
fuel of - a star is hydrogen.
- a white dwarf is helium.
|
| Q.5.
|
Which component of sunlight
facilitates drying of whet after harvesting ?
|
| Ans. |
Infra red.
|
| Q.6. |
A man found that he suffers
from repeated sneezing when ever he exposed to
dust. What could be the reason for such a
reaction ?
|
| Ans.
|
The
suffering person is allergic to dust.
|
| Q.7. |
Explain the role of roughage
in our food.
|
| Ans. |
Roughage
is the cellulose of plant cells - undisgestable
by our body, but it is helpful in digestion as
it increases the bulk of food, maintains the
movement of food through intestine and avoids
constipation by moistening the walls of
intestine. |
| Q.8. |
Which of the following
belonging to a food chain is likely to have
maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in
its body ?
Kingfisher, Zoophlankton, Fish,
Phytoplankton.
|
| Ans. |
Food
chain - Phyoplankton -- Zooplankton -- fish ---
Kingfisher. Kingfisher - Would have a
maximum concentration of harmful chemicals as it
is at the top of the formed food chain.
|
| Q.9.
|
Write the structural formula
of any one isomer of n-heptane (G7H16)
|
| Ans. |
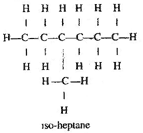
|
| Q.10. |
An astronomer claimed to
have discovered a pulsar in a distant galaxy.
Mention any one observation that he might have
made to claim his discovery.
|
| Ans. |
Emission
of radio waves from the centre of the circle in
which circle any star is moving with no visible
star in the centre.
|
| Q.11. |
Mention any four differences
between an external combustion engine and a
petrol engine.
|
| Ans. |
| External Combustion Engine
|
Internal Combustion Engine
|
| 1. It is
bulky is size.
|
1. It
can be made in any convenient size.
|
| 2. Fuel
burns out side the cylinder.
|
2. Fuel
burns inside the cylinder.
|
| 3. Mostly fuel is coal, wood
and furnace oil. |
3.
Mostly fuel is gasoline (petrol) or diesel.
|
4. Steam is generated in the
large boiler which make it risky to burst on
high pressure of steam.
|
4. A
controlled and small amount of fuel is burnt
into the cylinder, which does not make it risky
to burst i.e. It is safe.
|
|
| Q.12. |
Describe the process of
obtaining coke from coal. Name the gaseous by -
product obtained in this process.
|
| Ans. |
Destructive distillation
: Coke is obtained from coal by a simple process
known as destructive distillation in which coal
is heated in the absence of air.
Gaseous by - product - Coal
gas.
|
| Q.13. |
How are antibiotics
beneficial to us ? Name any two groups of
organisms from which they are obtained.
|
| Ans. |
Antibiotics -
Antibiotics are used to treat the bacterial
diseases viz. cholera, pneumonia, T.B. etc.
Antibiotics destroy the bacteria responsible for
disease without harming our body.
Name of group : Antibiotics
are obtained from Fungi and Bacteria.
|
| Q.14. |
Why is conservation of wild
life important ? Give any two reasons in support
of your answer.
|
| Ans.
|
1.Wild
life should be conserved to maintain the
ecological balance in nature. Wild life is
important link in food chain.
2. Wild life conservation is
important as it preserve the gene pool. It helps
to preserve the extinction of rare varieties of
birds and animals.
Wild life can be conserved
by adopting the following measure :
1. Hunting of wild animals
should be banned.
2. National parks and
sanctuaries should be established to provide
natural habitat to the wild animals and birds.
|
| Q.15. |
Explain the cleaning action
of soaps. |
| Ans.
|
Cleaning action of soaps
: Soap molecule possesses two ends, one
hydrocarbon end and the other - COONa end.
Hydrocarbon end is water repellant -
(Hydrophobic) while the COONa end is
bydrophillie ( water attracting). Soap solution
in water form miscelles i.e. they arrange
themselves radially such that hydrocarbon ends
inward and COONa end towards out. Hydrocarbon
end combines with dirt or grease particle and -
COONa end combines with water molecules, when
dirty cloth is wetted. During washing miscelles
remove the dirt from the wet surface and is
drained off with water flow.
|
| Q.16. |
List any four conditions
that are essential for the life to originate and
flourish on a planet. |
| Ans. |
The
following conditions are needed for the origin
and flourishment of life on a planet :
1. There should be present
building ( body building) blocks like elements
C,H,O,N,P etc. which may synthesise complex
compounds necessary for body building.
2. Proper temperature range
so that life sustaining chemical reactions may
occur.
3. Presence of a liquid
medium to transport nutrients like water.
4. Presence of protective
blanket to protect the life from ultra violet
rays from sunlight like ozone layer.
|
| Q.17. |
Heat produced on burning 5.0
g. or a fuel raises the temperature of 1.0 kg.
of water from 200
C 600C . If the
specific heat of water be 4.2J/g/0C. Calculate the
calorific value of the fuel.
|
| Ans. |
Mass of
fuel burnt = 5 g. Mass of water = 1.0 kg. =
1000g.
Change in temperature =
60-20 = 40deg.C
Sp heat of water =
4.2J/g/0C
Heat gained by water r= Heat
produced by fuel on burning.
He gained by water = m x s x
t = 1000g x 4.2 x 40deg. J.
Calorific value of fuel =
1000 x 4.2 x 40 / 1000 x 5 = 33.6 KJ/g.
|
| Q.18. |
With the help of a diagram
explain how the design of a box type solar
cooker ensures minimum loss of heat from its
inside.
|
| Ans. |
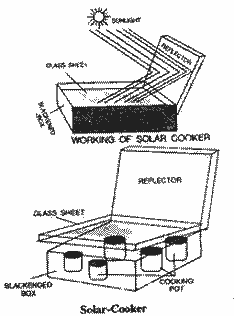
(i) The blacken inner
surface of the box absorbs heat reflected from
mirror. Heat loss to environment is prevented by
insulated box through conduction.
(ii) Heat loss through
radiation and convection is prevented by glass
sheet provided on the box.
|
| Q.19. |
A person decides to take
only milk and nothing else in his diet for a
year. Which one of the essential nutrient will
not be available to him ? Mention any two
symptoms of deficiency of this nutrient.
|
| Ans.
|
Vitamin
C. will not be available to the person.
Symptoms .(i) Swelling and
bleeding of fumes.
(ii) Loosening of teeth.
(iii) Pain in joints and
general weakness. |
| Q.20. |
Draw a diagram to show the
orbit of an artificial satellite of the earth.
Mark the position of apogee, perigee on it.
|
| Ans.
|
The following diagram is
displaying the position of above orbit :
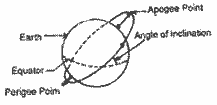
|
| Q.21. |
Describe sequentially the
processes, that led to the formation of
petroleum in nature, Name the aviation fuel used
in aeroplane jet engines.
|
| Ans. |
Formation of Petroleum - It is believed
that petroleum is formed formed micro -
organisms living in the sea.
(i) When these organisms
die, they sink to the bottom and are gradually
covered by sand and clay.
(ii) Over a period of
millions of years, these remains are converted
into hydrocarbons by heat, pressure and
catalytic action in the absence of air.
(iii) These hydrocarbons as
a mixture is petroleum which is found between
impermeable rocks.
Aviation Fuel - A special
Grade of Kerosene is used as aviation fuel in
aeroplane Jet engines.
|
| Q.22.
|
Describe the process of
generation of energy in the sun. Name the
scientist who was the first to propose this
explanation.
|
| Ans.
|
The
process by which energy is released in the Sun
in Nuclear fusion of hydrogen atoms in the core
of Sun. This process involves the combination of
hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei and releases
a huge amount of energy. This fusion reaction
started due to high temperature in the core,
caused by the contraction of core under
gravitational force of it.
Name of the Scientist : A
German physicist, Hans Beete' proposed that the
source of Sun energy is the nuclear fusion of
hydrogen in its core.
|
| Q.23. |
What is transplantation ?
What are its two advantages ? Name any two crops
that are usually grown by this method.
|
| Ans. |
Transplantation : Sees of some crops are
grown in a small part of field ( nursery). After
some growth the seedlings are transplanted in a
prepared field at proper distance. Later on
these seedlings grow and develop there.
This process is know as
transplantation.
Advantage : 1. Better and
healthy seedling are selected for cultivation by
this process.
2. Crops grow and develop
rapidly.
3. Proper distance can be
maintained between crop plants for their better
growth.
4. Weeds are left behind in
the nursery.
5. Roots penetrate the soil
better.
Name of crops : (i)
Paddy
(ii) Chilly
(iii) Brinjal, tomato,
onion. |
| Q.24. |
What is ten percent law ?
Explain with an example how energy flows through
different trophic levels ? |
| Ans. |
Ten percent law - Flow
of energy, in a food chain takes place by a law
known as 10 % from one trophic level to the next
trophic level.
According to 10 % law only 10 % of the
energy entering a particular trophic level is
available for transfer to the next higher
trophic level as 90 % of that is utilised by the
organism of that trophic level. In simple term
it is called as 10 % law.
Autotrophs ( green plants)
trap the sunlight and convert it to chemical
energy during photosynthesis which is stored in
the food manufactured by them.
They can utilize 1 % of
received sunlight only. When they receive 1000 J
energy, they will untilize only 10 J, while 990
J will be lost to the atmosphere in the form of
radiations. Now herbivores eat plants or their
products and will get only 10 J of energy from
plants. At this tropic level 9 J i.e. ( 90 % of
received energy) is utilized by herbivores in
their metabolic activities and lose it to the
environment in the form of hot and only a 10 %
part of received energy i.e. 1 J energy will be
available to the carnivores which feed on
herbivores. Similarly 10 % of energy of received
energy will flow to the successive tropic level.
Hence it is beneficial to have vegetarian habits
to get more energy.
|
| Q.25. |
With the help of a labelled
diagram describe the method of preparation of
methane in the laboratory. Is this gas
combustible ? How can you test this property ?
|
| Ans. |
Preparation of Methane :
Methane is pre pared in the laboratory by
heating sodium acetate and soda lime.
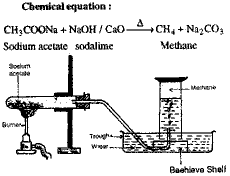
Test for combustibility - Fill up a
boiling tube with methane and bring a burning
splinter in the boiling tube containing methane
gas. Methane gas burns with a bluish flame.
|
| Q.26.
|
The mass of a star is 10
times that of the sun. Describe last two stages
in the life cycle. |
| Ans. |
When a
star has its initial mass much more than that of
the sun then it gets the following final stages
in its life after the end of red giant phase.
(i) Supernova : The core of helium formed
during the red giant phase would continue to
contract due to its own gravitation building up
higher and higher temperatures. As this
contraction continues the energy liberated
causes the outer envelope to explode with a
brilliant flash and it could release the same
amount of energy in one second as the sun
radiates in about a hundred years. Such
exploding star is called supernova.
This supernova explosion
liberates clouds of gases which would contribute
to the raw material for the formation of new
star.
(ii) Neutron Star : After supernova
explosion only core of star survives and
continue to contract resulting to a extremely
dense lump known as neutron star. Densities of
neutron star may be about million tonnes per
cubic centimeter.
(iii) Pular : a spinning neutron star emits
radiowaves and called pular.
|
| Q.27. |
Describe any three ways in
which biotic and biotic environment may cause
variation in the size of population of deers in
a forest.
|
| Ans. |
Following environment factors can cause
variation in the size of deers' population in a
forest.
(i) Nutrients supply : Supply of sufficient
grass by the forest will increase the size of
deers population while non-availability of
nutrients ( grass) will decrease it.
(ii) Available space : Sufficient
availability of space or forest favourable which
provides safe and flourishing environment, will
increase the size of population while the
adverse will decrease.
(iii) Interaction with other organism : Dense
population of predators ( like lion) will
decrease the population of dears in a forest by
eating them while the reverse will increase.
|
| Q.28. |
With the help of a labelled
diagram describe the process of extraction of
sulphur by Frasch process. |
| Ans. |
Extraction of Sulphur :
Sulphur is found in free state at the depth of
about 1000 feets in the soil. It is extracted by
the process 'Frasch Process'. A hole is bored to
the sulphur beds and three co-centric pipes an
pushed to the beds of sulphur. Since the melting
point of sulphur is (112.8 deg c) low and it is
insoluble in water, super heated water is forced
down through the outer most pipe. The heat of
water get it be melted. Now hot compressed air
is blown through the inner most pipe. By the
presence of compressed air molten sulphur comes
out at the surface of earth through middle pipe
in the form of froth ( Foams). |
| Q.29. |
The efficiency of a petrol
engine is 30 %. Calculate the power delivered by
it if it burns 0.03 kg. or petrol in one minute.
The calorific value of petrol is 50 KJ/g.
|
| Ans. |
Efficiency of engine = 30 %
Mass of petrol burnt = 0.03
kg. = 30 g.
Calorific value of petrol =
50 KJ/g.
Amount of energy liberated
by
30 g. petrol = 30 X 50 KJ.
Time = 4 min.
= 60 Sec.
Work done by engine = 30 x
30 x 50 /100 KJ.
Power delivered = 30 x 30 x
50 / 100 x 60 = 7.5 kw.
|
| Q.30. |
An element belonging to
group V of the Periodic Table is available in
nature in two forms, A and B. The ignition
temperature of A and B are 260 deg c and 30 deg.
c respectively. Identify the element. Name its
two forms. Name (i) the form that reacts with
concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide and
(ii) the one that would react with chlorine with
heating. Write the equations for the reactions
involved. |
| Ans.
|
Element - Element in
Phosphorus.
Form - form A is Red
Phosphorus.
Form B is yellow or white
phosphorus.
Reactions : - (i) Yellow Phosphorus reacts
with cone. Solution of sodium hydroxide.

|
| Q.31. |
State the factors that help
to determine that wheat crop has matured for
harvesting. Describe how biotic and abiotic
factors may affect the quality of stored grain.
Mention any two effects of each type of factors.
|
| Ans.
|
Factors
which determine the maturity of wheat crop for
harvesting.
1. The crop should have
absorbed all the necessary nutrients from the
mother plant.
2. The whole plant should
become some hard, dry and golden in colour.
3. The moisture content of
the grain should not be more than 14 % at the
time of harvesting to ensure safe storage. It
can be estimated by crushing some wheat grains
between the teeth, if it cracks, the moisture
content is just right for harvesting.
Biotic
factors - 1. Microbes - On being moisture
content more than 14 % of stored grain,
infestation of microbes - Bacteria and fungi,
damage the stored grains. The action of microbes
may result in loss of weight, decoloration,
heating, introduction of toxins and failure to
germinate.
2. Insects - some small insects like grain
borer, grain beetal, grain moth etc., may attack
stored food grains. Their infestation deplete
the food materials, nutritive components and
contaminate them with webs, cocoon and dead
remains.
Abiotic
Factor - 1. Moisture - Moisture content more
than 14 % of stored grain accelerates the attack
of insects and microbes which spoil and do the
grains even toxic.
2. Temperature - Temperature of stored
food grain is another significant factor for
safe storage. As the optimum temperature for
insects growth is 30 deg C to 32 deg C and 30
deg C to 40 deg C for micro organisms growth and
enzymatic action, so much temperature increases
the infestation of microbes, insects and
activates the enzymes responsible side for
spoilage of stored food grain.
|
| Q.32.
|
What is a nuclear reactor ?
Explain how nuclear fission reaction is
controlled in a reactor ? Mention any two
advantages and any two disadvantages of
harnessing nuclear energy.
|
| Ans. |
Nuclear reactor - It is
a device in which energy from controlled nuclear
fission reaction is obtained for useful
purposes.
Controlled chain reaction - When slow
moving neutron collides with the nucleus of
U-235, it make the nucleus of U-235 unstable and
breaks into two smaller nuclii of 94/36 Kr and
139/56 Ba. During this fission of nucleus a huge
amount of energy is released and three neutrons
set free which further break three more nuclei
of U-235 with a production of three times more
energy than the previous fission. Thus set free
three times neutrons in every fission break
three times more U-235 nuclii. A reaction occurs
in the form of chain known as chain reaction. In
very shores time a very very large amount of
energy liberates in an uncontrolled form.
To control the amount of
energy liberated, out of three neutrons, set
free during fission of U-235 nucleus, some are
absorbed by using neutron absorbant such as
cadmium, boron, graphite etc. the number of
fissions of U-235 nuclei are so made by
absorbing excess neutrinos that the energy
liberated remains controlled is called
controlled chain reaction.
Advantage - 1. It is a long lasting
rich and concentrated source of energy.
2. If some moderate
precautions are taken, it does not pollute air
like other resources' use viz. use of coal, oil,
wood etc.
Disadvantage - 1. There is an
additional danger of harmful wastes produced at
various steps of nuclear cycle which includes
mining, enrichment of ore and of course the
nuclear reaction inside the reactor. They emit
nuclear radiations which cause irrespective
damage to livings.
2. Always is a threat of
accident in reactor which releases harmful
radiations - B and Y ( gamma) rays.
|
| Q.33. |
State the three main steps
involved in metallurgical processes. Explain the
method of extraction of copper from its sulphide
ore. Write the chemical reactions involved.
|
| Ans. |
Metallurgical processes -
Following steps are involved in metallurgy.
1. Preliminary Treatment or Concentration
- Adopting different physical and chemical
methods gangue is removed from the ore in this
step.
2. Roasting and calcination - In this step
concentrated ore is heated in air or in the
absence of air to remove the volatile impurities
from the ore.
3. Reduction to metal - Metallic oxide,
obtained after roasting or calcination, is
reduced to metal by the use of a suitable
reducing agent.
4. Refining - Metal is purified in this
step up to the possible extent.
Extraction of copper : Following steps
are involved in the extraction of pure copper
from its ore :
(i) Concentration : Concentration of copper
is done by froth floatation process. Finally
powdered ore is mixed with water and a little
pine oil in a tank. Then air is bubbled through
the mixture. Concentrated ore is obtained as
froth ( Foam) on the top of water and impurities
are left at the bottom of the tank.
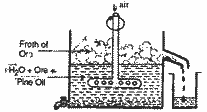
(ii) Roasting : Concentrated ore is then
heated bly in the presence of air. Volatile
impurities escape and CuS is oxidised to copper
oxide.
D
2CuS + 3O2
--------------- 2CuO + 2SO2
(iii) Reduction : Cuo formed during roasting
is mixed with suitable more amount of
concentrated ore, in this way copper is
obtained. It is known as blister copper as
eruptions are found on its surface due to
escaping -
CuS + 2CuO --
3Cu + SO2
CuO can be reduced by coke also.
D
2CuO + C -------- 2Cu + CO2
Coke
(iv) Refining : Pure copper is obtained by
electrolysis. Purecopper is obtained by
electrolysis. Pure metallic wire is used as
cathode, impure copper rod is used as Anode and
CuSO4 is taken as
electrolyte. when electricity is passed through
electrolyte pure copper deposits at cathode
while impurities are left at the bottom of the
cell near anode.
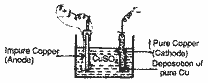
|